This article is written by Bevan Christian, Software Engineer @ IDN Engineering
This article was origninally published here.
In this article, we’re spilling the beans on why we switched from Azure to Codemagic and showing you exactly how to supercharge your CI/CD game. We’re covering the entire spectrum — from compiling and creating release notes to testing and deployment. Let’s rewind a bit to our iOS developers’ struggles. Our CI process (think builds, tests, and coverage) was taking a chunky 40–50 minutes. Even after briefly dipping to 30 minutes, it shot back up due to new features and libraries, putting the brakes on our development speed. And guess what? CD (build and deploy) wasn’t any better, sapping 40 minutes.
Before we dive in, make sure you’re comfortable with Fastlane and have some CI/CD experience under your belt.
Codemagic to the Rescue!
But hold on, Codemagic to the rescue! The magic ingredient? M1 architecture. It turbocharged our build time, shrinking the total ordeal to just 25 minutes, down from the 80–90-minute marathon.
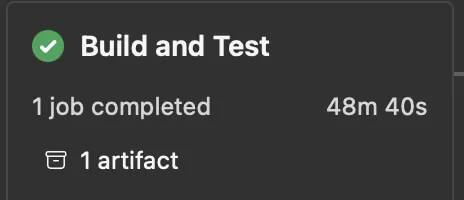

Witness the Marvel: A Whopping 76.85% Boost in Our CI/CD Process! 🚀
Our Script
Now, here’s a sneak peek into the goods — a snippet of YAML code for your iOS exploits, complete with testing, building, and the grand finale, deploying to Firebase Distribution.
definitions:
- &installDependency
name: Install Dependency
script: |
gem install bundler
bundle install
- &runTest
name: Run Unit Test
script: |
bundle exec fastlane pr_tests_codemagic
- &podInstall
name: Install CocoaPods dependencies
script: |
pod install
build-to-firebase-distribution:
name: publish-to-firebase-distribution
max_build_duration: 35
instance_type: mac_mini_m1
cache:
cache_paths:
- $HOME/Library/Caches/CocoaPods
environment:
groups:
- iosVariable
- firebase_credentials
ios_signing:
provisioning_profiles:
- AdHocMobileProvisionCodemagic
certificates:
- distributionCertificate
vars:
BUNDLE_ID: "com.app.App"
XCODE_WORKSPACE: "app.xcworkspace"
XCODE_SCHEME: "release"
TARGET_NAME: "your app name"
APP_STORE_APPLE_ID: xxxx
xcode: 14.2
cocoapods: default
scripts:
- *installDependency
- *podInstall
- *runTest
- name: Generate release notes
script: |
cd $CM_BUILD_DIR
now=$(date)
currentDate="Current build on $now, This log may not be a complete log, contact developer for the complete build log"
echo $currentDate >> ./release_notes.txt
echo "XCODE_SCHEME: $XCODE_SCHEME" >> ./release_notes.txt
git log --graph --oneline --pretty=format:"%s" --since="yesterday" >> ./release_notes.txt
cat ./release_notes.txt
- name: Set up provisioning profiles settings on Xcode project
script: xcode-project use-profiles
- name: Get the latest build number and Increment build number
script: |
LATEST_BUILD_VERSION=$(firebase-app-distribution get-latest-build-version -p xxx -a 1:xxx:ios:xxx)
cd $CM_BUILD_DIR # avgtool must run in the folder where xcodeproj file is located
agvtool new-version -all $(($LATEST_BUILD_VERSION + 1))
- name: Build ipa for distribution
script: |
xcode-project build-ipa -v\
--workspace "$CM_BUILD_DIR/$XCODE_WORKSPACE" \
--clean \
--scheme "$XCODE_SCHEME" \
--archive-flags="-destination 'generic/platform=iOS'"
artifacts:
- build/ios/ipa/*.ipa
- /tmp/xcodebuild_logs/*.log
- $HOME/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/**/Build/**/*.app
- $HOME/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/**/Build/**/*.dSYM
publishing:
firebase:
firebase_service_account: $FIREBASE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT
ios:
# Add your iOS app id retrieved from Firebase console
app_id: "1:xxx:ios:xxxx"
# Add one or more groups that you wish to distribute your iOS application to.
# You can create groups in the Firebase console
groups:
- ios-tester
Fastfile
desc "Run Pull Request tests Codemagic"
lane :pr_tests_codemagic do
scan(
workspace: "app.xcworkspace",
scheme: "UnitTesting",
device: "iPhone SE (3rd generation)",
reset_simulator: true,
configuration: "debug",
test_without_building: false,
skip_build: false,
fail_build: false,
number_of_retries: 3,
concurrent_workers: 4
)
if $?.exitstatus != 0
UI.user_error!("Tests failed. Exiting with status 1.")
exit(1)
else
UI.success("Tests passed.")
end
end
This YAML configuration is for setting up a CI/CD pipeline using Codemagic for an iOS application. It defines a scheduled build named scheduled-build-to-firebase-distribution-RC. The build process includes several steps, such as installing dependencies, running tests, generating release notes, setting up provisioning profiles, incrementing build numbers, setting up code signing, and building the IPA for distribution.
Build environment
The build is performed on a mac_mini_m1 instance.
Cache
cache:
cache_paths:
- $HOME/Library/Caches/CocoaPods
CocoaPods caching is used to speed up dependency installation.
Environment Variables
environment:
groups:
- iosVariable
- firebase_credentials
Various environment variables are defined for the build process, including BUNDLE_ID, XCODE_WORKSPACE, XCODE_SCHEME, TARGET_NAME, and APP_STORE_APPLE_ID. All these environment variables can be set in your app settings in the Codemagic web app.
iOS code signing
Code signing is a crucial security mechanism in the iOS app development process. It involves adding a digital signature to your app’s executable and other relevant files to verify its authenticity and ensure that it hasn’t been tampered with. Code signing is essential for app distribution and installation on iOS devices.
Certificate: Developers generate a request and receive a digital certificate from Apple. This certificate confirms their identity and links their public key to their developer account.
Provisioning Profile: A setup file that defines app details, device access, and distribution method. Different types, like development and distribution profiles, are tied to the certificate.
ios_signing:
provisioning_profiles:
- AdHocMobileProvisionCodemagic
certificates:
- distributionCertificate
Since I will publish this app to Firebase Distribution, I will need to use an Ad Hoc profile. If I publish to App Store or TestFlight, I should use App Store profiles.
To manage this certificate you can go to Team settings -> Integrations.
- Add your App Store Connect API Key
After you successfully add the App Store Connect API Key you can proceed to Team settings -> Code signing identities.
- Upload your .p12 file. In my case i will name it
distributionCertificate
- After that, fetch your profile — in my case, I will name it
AdHocMobileProvisionCodemagic. When fetching profiles, you’ll need an API key from App Store Connect.
Additional Scripts
Several scripts are executed during the build process:
Install Dependency
Installs the Bundler gem and installs Ruby dependencies using bundle install.
Install CocoaPods dependencies
Installs CocoaPods dependencies using pod install.
Run Unit Test
Executes unit tests using Fastlane and the specified lane pr_tests_codemagic.
Generate Release Notes
Creates release notes by appending build information, Xcode scheme, and recent commit messages to a text file.
- name: Generate release notes
script: |
cd $CM_BUILD_DIR
now=$(date)
currentDate="Current build on $now, This log may not be a complete log, contact developer for the complete build log"
echo $currentDate >> ./release_notes.txt
echo "XCODE_SCHEME: $XCODE_SCHEME" >> ./release_notes.txt
git log --graph --oneline --pretty=format:"%s" --since="yesterday" >> ./release_notes.txt
Here’s an explanation:
cd $CM_BUILD_DIR: This changes the current directory to the$CM_BUILD_DIR, which is a predefined environment variable by Codemagic representing the directory where the build is taking place.now=$(date): This captures the current date and time using thedatecommand and assigns it to the variablenow.currentDate="Current build on $now, This log may not be a complete log, contact developer for the complete build log": This creates a message indicating the current build timestamp and a note that the log might not be complete, encouraging others to contact the developer for a full log. The variable$nowis substituted with the captured date and time.echo $currentDate >> ./release_notes.txt: This appends the currentDate message to a file namedrelease_notes.txt.echo "XCODE_SCHEME: $XCODE_SCHEME" >> ./release_notes.txt: This appends the value of theXCODE_SCHEMEenvironment variable to therelease_notes.txtfile. TheXCODE_SCHEMEis likely a scheme name used in the Xcode project.git log --graph --oneline --pretty=format:"%s" --since="yesterday" >> ./release_notes.txt: This command retrieves the commit history using git log. Commit messages from the Git history, starting from yesterday, are added to the notes file.
Increment build number
Get the latest build number and Increment build number
script: |
LATEST_BUILD_VERSION=$(firebase-app-distribution get-latest-build-version -p xxx -a 1:xxx:ios:xxx)
cd $CM_BUILD_DIR # avgtool must run in the folder where xcodeproj file is located
agvtool new-version -all $(($LATEST_BUILD_VERSION + 1))
Here’s an explanation:
LATEST_BUILD_VERSION=$(firebase-app-distribution get-latest-build-version -p xxx -a 1:xxx:ios:xxx): Fetches the latest build version from Firebase.cd $CM_BUILD_DIR: Navigates to the build directory where the Xcode project file is located.agvtool new-version -all $(($LATEST_BUILD_VERSION + 1)): Increases the build version by 1 usingagvtool, ensuring a unique identifier for the new build.
Set up code signing settings on Xcode project
- name: Set up provisioning profiles settings on Xcode project
script: xcode-project use-profiles
Configures provisioning profiles on the Xcode project.
Build IPA for distribution
xcode-project build-ipa -v\
--workspace "$CM_BUILD_DIR/$XCODE_WORKSPACE" \
--clean \
--scheme "$XCODE_SCHEME" \
--archive-flags="-destination 'generic/platform=iOS'"
Builds the IPA file for distribution, specifying the workspace, scheme, and archive flags.
This script is provided by Codemagic, you can check the documentation here.
Publishing
publishing:
firebase:
firebase_service_account: $FIREBASE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT
ios:
# Add your iOS app id retrieved from Firebase console
app_id: "1:xxx:ios:xxxx"
# Add one or more groups that you wish to distribute your iOS application to.
# You can create groups in the Firebase console
groups:
- ios-tester
This script is for publishing to Firebase Distribution, where $FIREBASE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT is an environment variable that I’ve set in the firebase_credentials environment variable group. The app ID can be found in the Firebase console under Project settings -> Your Apps Section. For the complete documentation, you can refer to this link:
https://docs.codemagic.io/yaml-publishing/firebase-app-distribution/.
Conclusion
To sum it up, Codemagic’s M1-powered prowess is our secret sauce for a speedier CI/CD journey. This article unwraps the tech wizardry that slashed build times and ramped up our development mojo. We’re keeping things simple, showing how our YAML wizardry choreographs tests, builds, and deployments like a symphony of efficiency.
P.S. This article was written when the M1 machines were launched at Codemagic. However, Apple Silicon M2 machines are now available for even faster builds!




















Discussion about this post