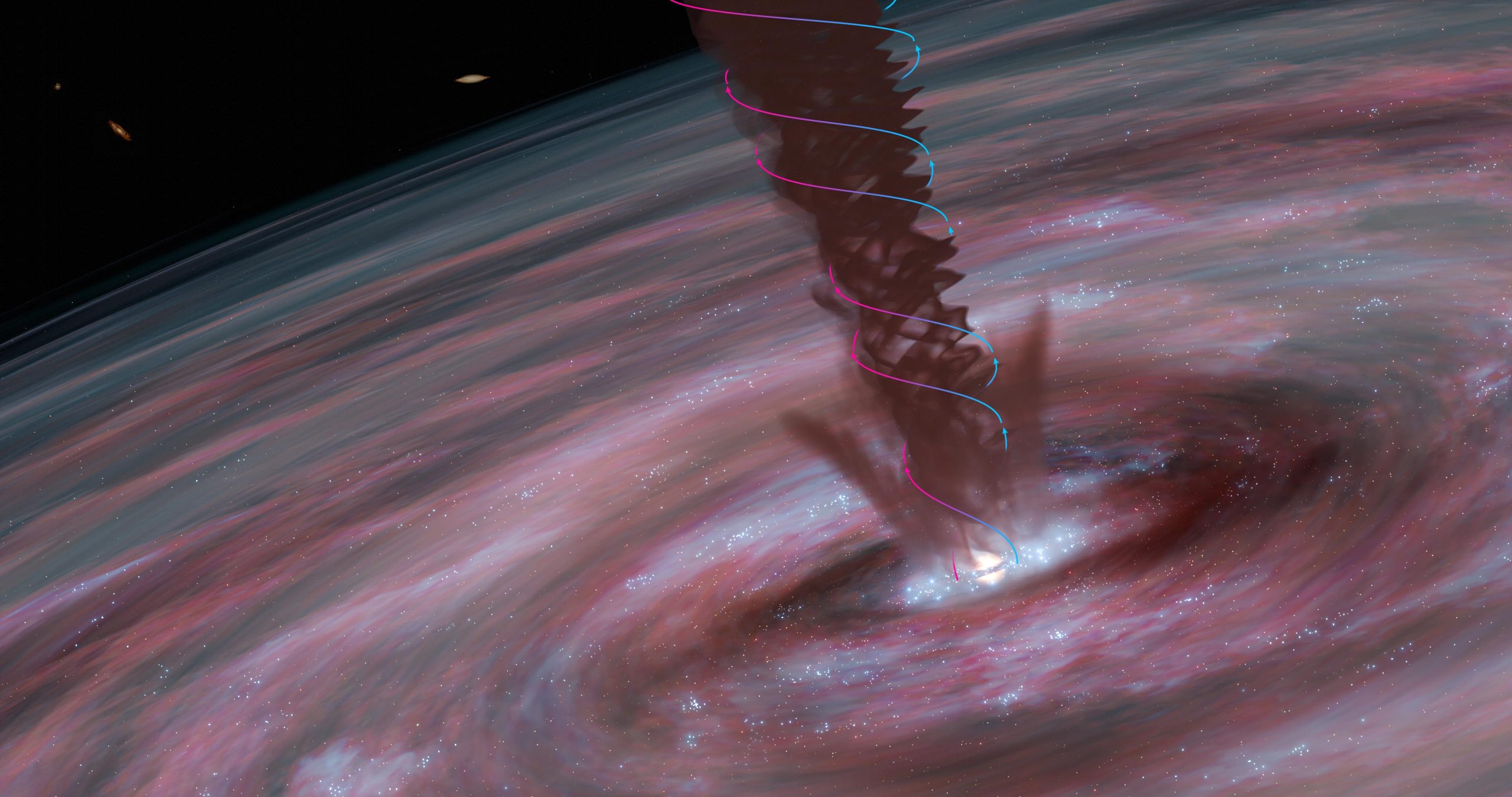
A spiraling wind helps the supermassive black hole in galaxy ESO320-G030 to grow, assisted by magnetic fields. In this illustration, the core of the galaxy is dominated by a rotating wind of dense gas leading outwards from the (hidden) supermassive black hole at the galaxy’s very center. Colored lines with arrows show the motions of the gas traced by light from molecules of hydrogen cyanide and seen with the ALMA telescope (blue indicated motion towards us and red away). Credit: M.D. Gorski/Aaron Geller/Northwestern University/CIERA
Scientists identified a magnetized wind in a nearby galaxy that supports the growth of its central supermassive 
Mark Gorski, Department of Space, Earth and Environment, Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden; and Northwestern University, USA. Credit: Chalmers University of Technology | Christian Löwhagen
In search of clues to this mystery, a team of scientists led by Mark Gorski (
Susanne Aalto, Professor, Department of Space, Earth and Environment, Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden. Credit: Chalmers University of Technology | Anna-Lena Lundqvist
“We can see how the winds form a spiraling structure, billowing out from the galaxy’s center. When we measured the rotation, mass, and velocity of the material flowing outwards, we were surprised to find that we could rule out many explanations for the power of the wind, star formation for example. Instead, the flow outwards may be powered by the inflow of gas and seems to be held together by magnetic fields,” says Susanne Aalto.
The Role of Magnetic Fields in Galactic Processes
The scientists think that the rotating magnetic wind helps the black hole to grow.
Material travels around the black hole before it can fall in – like water around a drain. Matter that approaches the black hole collects in a chaotic, spinning disk. There, magnetic fields develop and get stronger. The magnetic fields help lift matter away from the galaxy, creating the spiraling wind. Losing matter to this wind also slows the spinning disk – that means that matter can flow more easily into the black hole, turning a trickle into a stream.
Galactic Winds: A Comparative Perspective
For Mark Gorski, the way this happens is strikingly reminiscent of a much smaller-scale environment in space: the swirls of gas and dust that lead up to the birth of new stars and planets.
“It is well-established that stars in the first stages of their evolution grow with the help of rotating winds – accelerated by magnetic fields, just like the wind in this galaxy. Our observations show that supermassive black holes and tiny stars can grow by similar processes, but on very different scales,” says Mark Gorski.
Future Research and Unsolved Mysteries
Could this discovery be a clue to solving the mystery of how supermassive black holes grow? In the future, Mark Gorski, Susanne Aalto, and their colleagues want to study other galaxies that may harbor hidden spiraling outflows in their centers.
“Far from all questions about this process are answered. In our observations, we see clear evidence of a rotating wind that helps regulate the growth of the galaxy’s central black hole. Now that we know what to look for, the next step is to find out how common a phenomenon this is. And if this is a stage which all galaxies with supermassive black holes go through, what happens to them next?” asks Mark Gorski.
For more on this research, see Magnetic Winds Drive Black Hole Growth in Nearby Galaxy.
Reference: “A spectacular galactic scale magnetohydrodynamic powered wind in DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202348821
More about the ALMA telescope:
- The Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), an international astronomy facility, is a partnership of ESO, the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) and the National Institutes of Natural Sciences (NINS) of Japan in cooperation with the Republic of Chile. ALMA is funded by ESO on behalf of its Member States, by NSF in cooperation with the National Research Council of Canada (NRC) and the National Science and Technology Council (NSTC) in Taiwan and by NINS in cooperation with the Academia Sinica (AS) in Taiwan and the Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute (KASI).
- ALMA construction and operations are led by ESO on behalf of its Member States; by the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO), managed by Associated Universities, Inc. (AUI), on behalf of North America; and by the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ) on behalf of East Asia. The Joint ALMA Observatory (JAO) provides the unified leadership and management of the construction, commissioning and operation of ALMA.
- Chalmers University of Technology and Onsala Space Observatory have been involved in ALMA since its inception; receivers for the telescope are one of many contributions. Onsala Space Observatory is host to the Nordic Alma Regional Centre, which provides technical expertise to the Alma project and supports astronomers in the Nordic countries in using Alma.
The researchers involved in the study are Mark Gorski, Susanne Aalto, Sabine König, Clare F. Wethers, Chentao Yang, Sebastien Muller, Kyoko Onishi, Mamiko Sato, Niklas Falstad, J. G. Mangum, S. T. Linden, F. Combes, S. Martín, M. Imanishi, K. Wada, L. Barcos-Muñoz, F. Stanley, S. García-Burillo, P. P. van der Werf, A. S. Evans, C. Henkel, S. Viti, N. Harada, T. Díaz-Santos, J. S. Gallagher and E. González-Alfonso.
At the time of the study, the researchers were active at: Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden; National Radio Astronomy Observatory, USA; University of Massachusetts at Amherst, USA; PSL University, France; European Southern Observatory, Chile; National Astronomical Observatory of Japan; Kagoshima University, Japan; University of Virginia, USA; Institut de Radioastronomie Millimétrique (IRAM), France; Observatorio Astronómico Nacional (OAN-IGN), Spain; Leiden University, The Netherlands; Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie, Germany; Chinese Academy of Sciences, PR China; King Abdulaziz University,




















Discussion about this post