Some content in this post might be outdated. It was written before Codemagic became from a Flutter CI/CD to a CI/CD
for all mobile app platforms after introducing codemagic.yaml.
Mar 31, 2019
This article was originally published on Medium by George Herbert
See also the video guide on YouTube by Jonas de Vrient
Thank you so much for sharing your knowledge with the Flutter community🙏
PS! If you want to be a guest writer for Codemagic, let us know. We are more than happy to share your tutorial or case study with more than 10K Codemagic followers.
The Problem
I was setting up the repository on GitHub and the CI on Codemagic for my new Flutter project, which would be using Firebase. I was about to make my initial commit and it hit me. I do not want to put the config JSON (Android) or plist (iOS) on GitHub for the world to see. (It is currently private, but if I open-sourced the project, the details may be in the commit history). So the problem is this. How do I import these files into my CI/CD pipeline to be used as part of the build ready for testing and deployment?
Initially, I thought about storing the files in a separate repository (or a secure location) then clone and move the files into place. Though able, I felt like it required too much scripting for something that should be relatively simple. I must be missing a trick…
I was.
Disclaimer: This all stemmed from an initial pointer on the Codemagic Slack link here.
The Solution
Prerequisites
- Created a Firebase project and have the Android and/or iOS config files
- Codemagic project
Step 1 — Encode Firebase config files
Codemagic allows variables to be set up in a workflow which can be used in any part of the build or test process. By using base64 (what is base64?) you can load a JSON file or a plist into a string with no spaces. This makes it easier to assign to variables in scripts.
First off, navigate in the command line to the folder that has your config files in. Most likely one of these, depending on whether it is Android or iOS:
$PROJECT_ROOT/android/app/google-services.json
$PROJECT_ROOT/ios/Runner/GoogleService-Info.plist
Once in the folder, encode the file’s contents, following the section for your OS or preference.
Base64 is the same on all machines so you have a few options for creating encoded strings, which I will detail below.
Mac
openssl base64 -in GoogleService-Info.plist #ios
openssl base64 -in google-services.json #android
Linux
Windows
It seems you have to create a file as output. You will just need the output file’s contents for the next step.
certutil -encode inputFileName encodedOutputFileName
Web
Use at your discretion. I do not know what they do with the data they encode — I would not recommend this method foot anything enterprise/business related but hobby projects may be ok but try one of the above options first.
Step 2 — Create environment variable(s) in the workflow
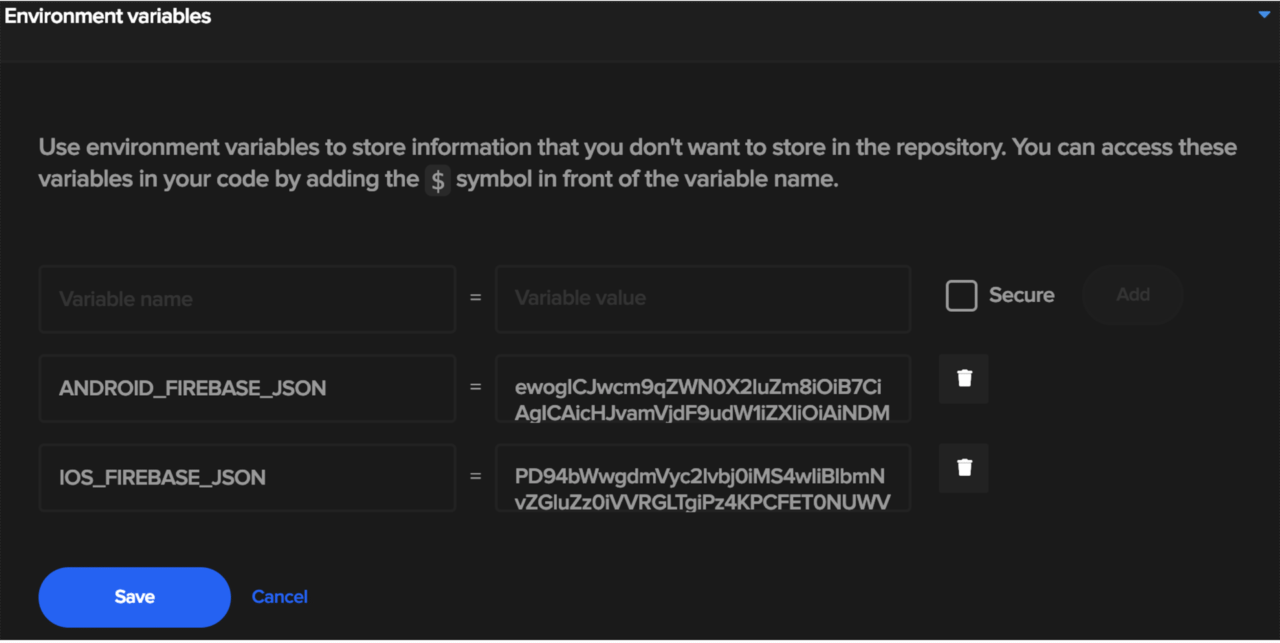
Now that you have the encoded values from step 1. Got to Codemagic. Open your project and got to “Settings” and click and expand “Environment Variables”.
Enter the name of the variables you wish into “variable name” then paste the base64 encoded values in the “variable value”.
Tip: Make sure you click the tick to the right of the value box when you are done. Otherwise, these will not be saved, when you click save.
Once all values are confirmed click “Save”.
Step 3 — Decode and Create File for Build
In the pre-build section of your workflow (works in other sections if you would prefer). Click the “+” icon and in the expanded area enter the following (ensuring the environment variable names match that of the ones you created in step 2).
#!/bin/sh
echo $ANDROID_FIREBASE_JSON | base64 --decode
> $CM_BUILD_DIR/android/app/google-services.json
echo $IOS_FIREBASE_JSON | base64 --decode
> $CM_BUILD_DIR/ios/Runner/GoogleService-Info.plist
Once entered it should look something like this.
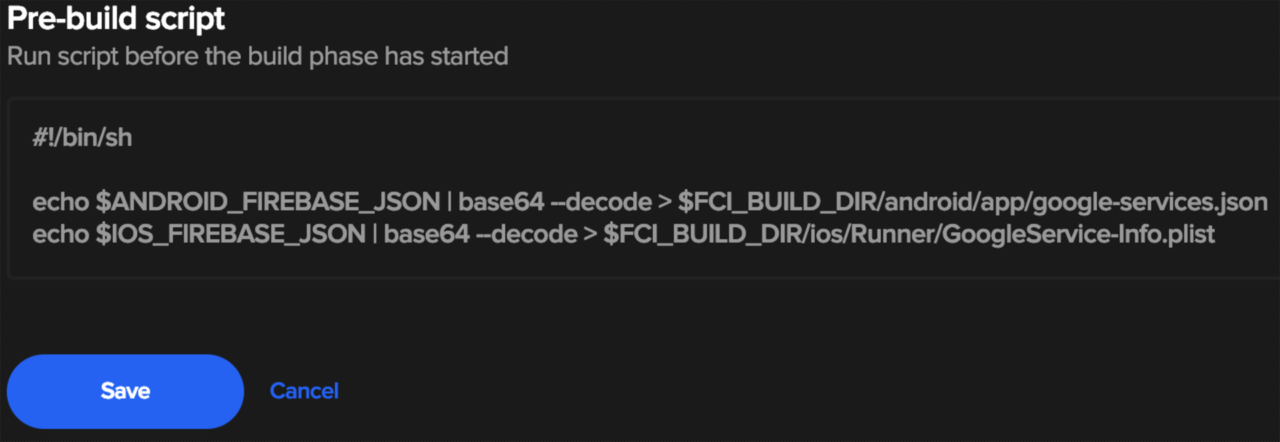
Once happy, click “Save”.
Step 4 — Done!
You are good to go. Go and click “Build” and watch the magic happen!
A Little Bonus
If you want to have the files in your project locally but do not want to commit them to GitHub (or other), just add the following to your .gitignore file.
# Firebase
/android/app/google-services.json
/ios/Runner/GoogleService-Info.plist
Conclusion
The use of environment variables combined with base64 can result in some quite useful additions allowing for more flexible workflows — for examples, development build, production build etc.
Any questions feel free to comment or Slack me (George Herbert) on the Codemagic Slack.
George Herbert is a Software Engineer for 5+ Years in Java, Scala, Python
Scala Developer By Day
Flutter Developer By Night
Occasional Blog Post Writer
Check out Jonas De Vrient’s webpage and contact him via GitHub.










![How to load Firebase config in Codemagic with environment variables [Video] How to load Firebase config in Codemagic with environment variables [Video]](https://blog.codemagic.io/uploads/covers/CM_Firebase-config.png)






%20(2)%20(1).jpg)

Discussion about this post