Visualization of the bridge recombinase mechanism. Credit: Visual Science
Arc Institute scientists have discovered the bridge recombinase mechanism, a revolutionary tool that enables fully programmable 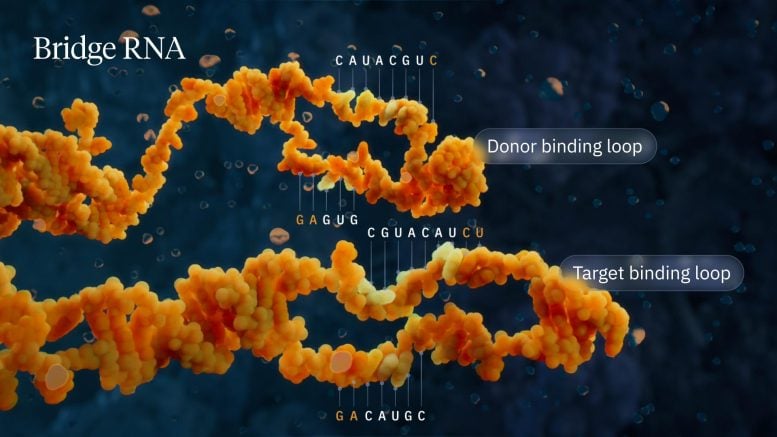
Visualization of the bridge recombinase mechanism highlighting the donor and target binding loops. Credit: Visual Science
A New Era of Genetic Programming
“The bridge RNA system is a fundamentally new mechanism for biological programming,” said Dr. Patrick Hsu, senior author of the study and an Arc Institute Core Investigator and 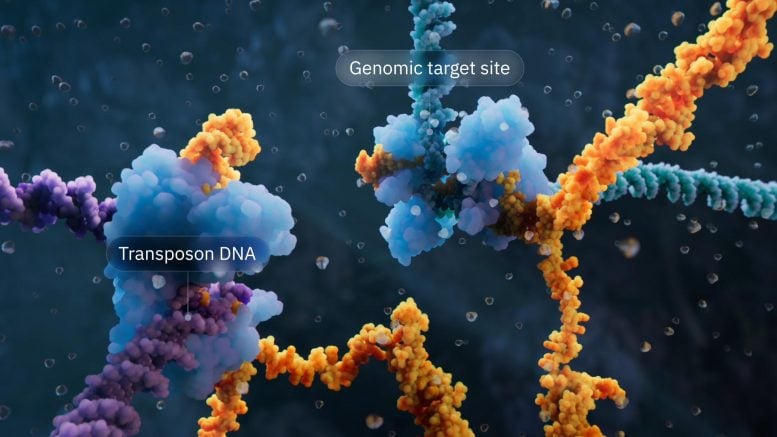
Visualization of the bridge recombinase mechanism highlighting the transposon DNA and Genomic Target site. Credit: Visual Science
Advanced Mechanism of Bridge RNA
The Hsu lab found that when IS110 excises itself from a genome, the non-coding DNA ends are joined together to produce an RNA molecule – the bridge RNA – that folds into two loops. One loop binds to the IS110 element itself, while the other loop binds to the target DNA where the element will be inserted. The bridge RNA is the first example of a bispecific guide molecule, specifying the sequence of both target and donor DNA through base-pairing interactions.
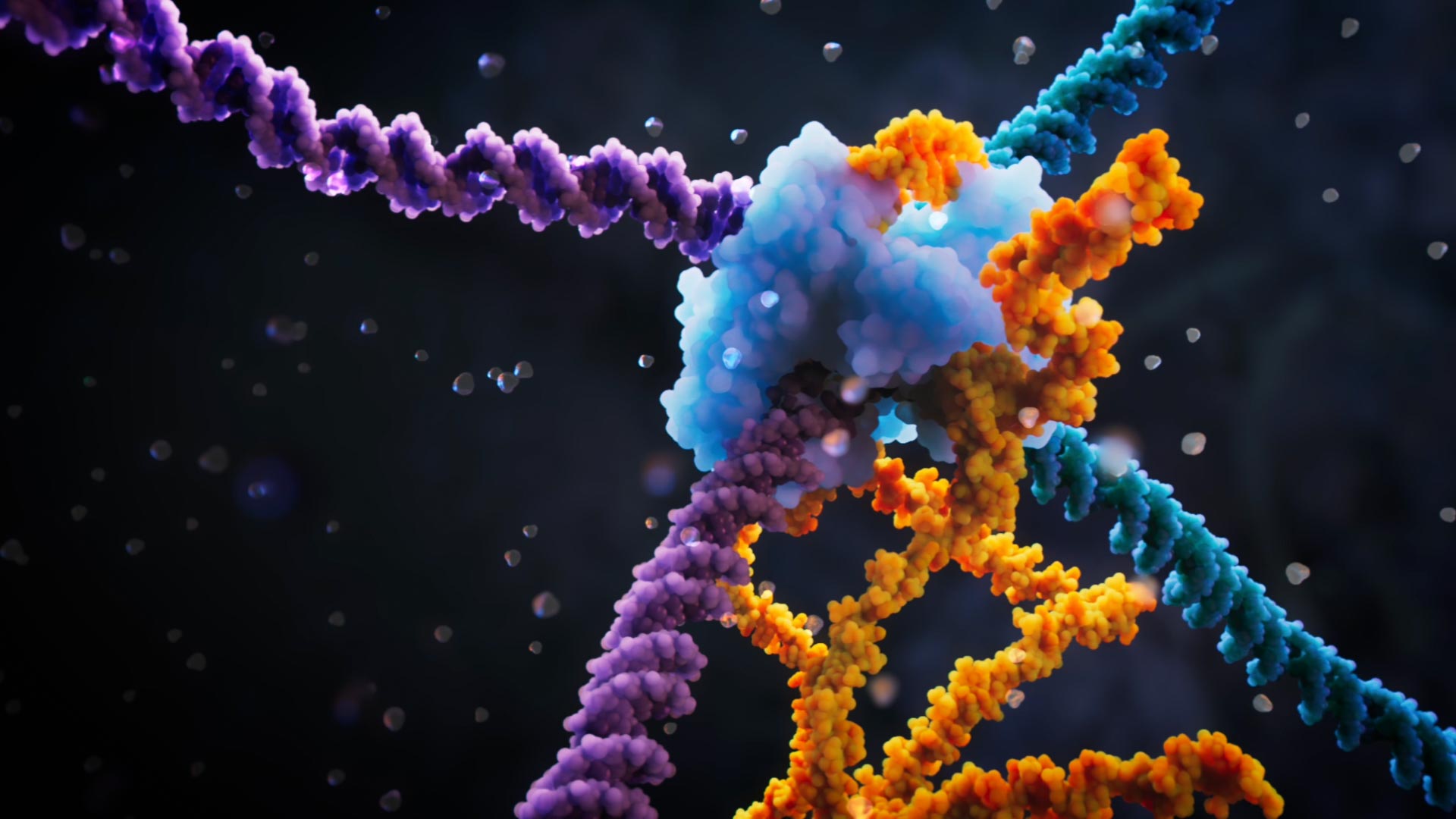
A team of researchers from the Arc Institute have discovered the bridge recombinase mechanism, a precise and powerful tool to recombine and rearrange DNA in a programmable way. Going far beyond programmable genetic scissors like CRISPR, the bridge recombinase mechanism enables scientists to specify not only the target DNA to be modified, but also the donor material to be recognized, so they can insert new, functional genetic material, cut out faulty DNA, or invert any two sequences of interest. Discover more in this short video visualizing the key aspects of the bridge recombination mechanism. Credit: Visual Science
Each loop of the bridge RNA is independently programmable, allowing researchers to mix and match any target and donor DNA sequences of interest. This means the system can go far beyond its natural role that inserts the IS110 element itself, instead enabling insertion of any desirable genetic cargo—like a functional copy of a faulty, disease-causing gene—into any genomic location. In this work, the team demonstrated over 60% insertion efficiency of a desired gene in E. coli with over 94% specificity for the correct genomic location.
“These programmable bridge RNAs distinguish IS110 from other known recombinases, which lack an RNA component and cannot be programmed,” said co-lead author Nick Perry, a UC Berkeley bioengineering graduate student. “It’s as if the bridge RNA were a universal power adapter that makes IS110 compatible with any outlet.”

Patrick Hsu, Nick Perry and Matt Durrant discuss the newly discovered bridge recombinase mechanism. Credit: Ray Rudolph
Collaborative Research and Future Implications
The Hsu lab’s discovery is complemented by their collaboration with the lab of Dr. Hiroshi Nishimasu at the University of Tokyo, also published on June 26 in Nature. The Nishimasu lab used cryo-electron microscopy to determine the molecular structures of the recombinase-bridge RNA complex bound to target and donor DNA, sequentially progressing through the key steps of the recombination process.

Januka Athukoralage, Nicholas Perry, Silvana Konermann, Matthew Durrant, Patrick Hsu, James Pai and Aditya Jangid. Credit: Ray Rudolph
With further exploration and development, the bridge mechanism promises to usher in a third generation of RNA-guided systems, expanding beyond the DNA and RNA cutting mechanisms of CRISPR and RNA interference (RNAi) to offer a unified mechanism for programmable DNA rearrangements. Critical for the further development of the bridge recombination system for mammalian genome design, the bridge recombinase joins both DNA strands without releasing cut DNA fragments – sidestepping a key limitation of current state-of-the-art genome editing technologies.
“The bridge recombination mechanism solves some of the most fundamental challenges facing other methods of genome editing,” said research co-lead Matthew Durrant, a senior scientist at Arc. “The ability to programmably rearrange any two DNA molecules opens the door to breakthroughs in genome design.”
References:
“Bridge RNAs direct programmable recombination of target and donor DNA” by Matthew G. Durrant, Nicholas T. Perry, James J. Pai, Aditya R. Jangid, Januka S. Athukoralage, Masahiro Hiraizumi, John P. McSpedon, April Pawluk, Hiroshi Nishimasu, Silvana Konermann and Patrick D. Hsu, 26 June 2024, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07552-4
“Structural mechanism of bridge RNA-guided recombination” by Masahiro Hiraizumi, Nicholas T. Perry, Matthew G. Durrant, Teppei Soma, Naoto Nagahata, Sae Okazaki, Januka S. Athukoralage, Yukari Isayama, James J. Pai, April Pawluk, Silvana Konermann, Keitaro Yamashita, Patrick D. Hsu and Hiroshi Nishimasu, 26 June 2024, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07570-2










/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/34/31/3431771d-41e2-4f97-aed2-c5f1df5295da/gettyimages-1441066266_web.jpg)








Discussion about this post