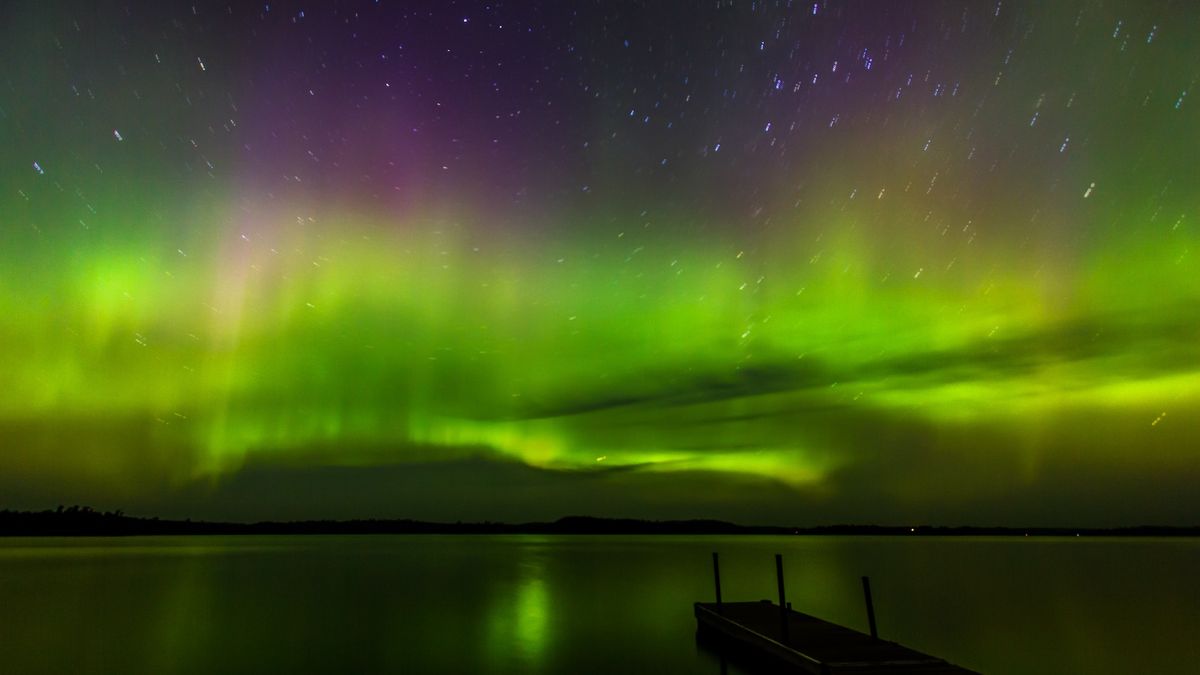
Tonight (Aug. 1) may be the last chance for skywatchers in parts of the U.S. to see the northern lights triggered by a powerful “cannibal” solar eruption that’s crackling through our planet’s atmosphere.
The northern lights — also known as the aurora borealis — may be visible tonight in parts of northern Washington, Idaho, Montana, North and South Dakota, Minnesota, Wisconsin, Michigan, New York and Maine, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Prediction Center. These are much lower latitudes than the ethereal light shows are typically seen.
Meanwhile, far more intense auroral displays are likely to be visible in northern Canada and Alaska.
To see if a region near you falls within the predicted aurora viewing zone, check out NOAA’s latest aurora forecast map below:
Tonight’s auroras are the result of several powerful blasts of solar radiation that hit our planet’s atmosphere on Tuesday and Wednesday (July 30 and 31). These hot, fast-moving globs of solar particles are known as coronal mass ejections (CMEs), and they occur when tangled magnetic field lines on the sun suddenly snap and then realign, thus flinging wads of plasma into space.
Related: 32 stunning photos of auroras seen from space
When a CME hits Earth, those solar particles skate along our planet’s own magnetic field lines toward the North and South Poles, charging up molecules in the atmosphere along the way and causing them to emit energy in the form of colorful light. Stronger CMEs tend to produce more widespread auroras; in May, for example, the most powerful geomagnetic storm in more than 20 years produced auroras that were visible as far south as Florida.
Tonight’s auroras won’t reach such impressive extremes — but, they do originate from a stronger-than-usual “cannibal” solar explosion. Before reaching Earth earlier this week, two back-to-back CMEs combined in space, while still in transit to our planet. There, they gobbled each other up, turning into a single massive “cannibal CME” that rattled our planet’s magnetosphere on Tuesday. A chain of smaller CMEs then hit our planet on Wednesday, according to NOAA, leaving tonight’s auroras as an after-effect.
If you can’t see tonight’s auroras, more are predicted to appear at similar latitudes this weekend after another CME hits Earth around midday Saturday (Aug. 3), according to NOAA’s latest forecast.
In general, CMEs, and by extension auroras, are far more common during the peak of the sun’s 11-year activity cycle, known as solar maximum. Some scientists predict the sun is already in this phase now, and that it could continue to peak for the remainder of the year. Expect more chances to see the northern lights dance later this year.
The best way to view auroras is by finding a dark place far from artificial lights. (Use a light pollution map if you aren’t sure where to go.) In summer in the Northern Hemisphere, you may have to wait until around midnight for the sky to be suitably dark. Strong auroras are visible to the naked eye, but the camera on your cell phone may be even more sensitive to the shimmering lights than your eyes are.













/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/d1/82/d18228f6-d319-4525-bb18-78b829f0791f/mammalevolution_web.jpg)






Discussion about this post