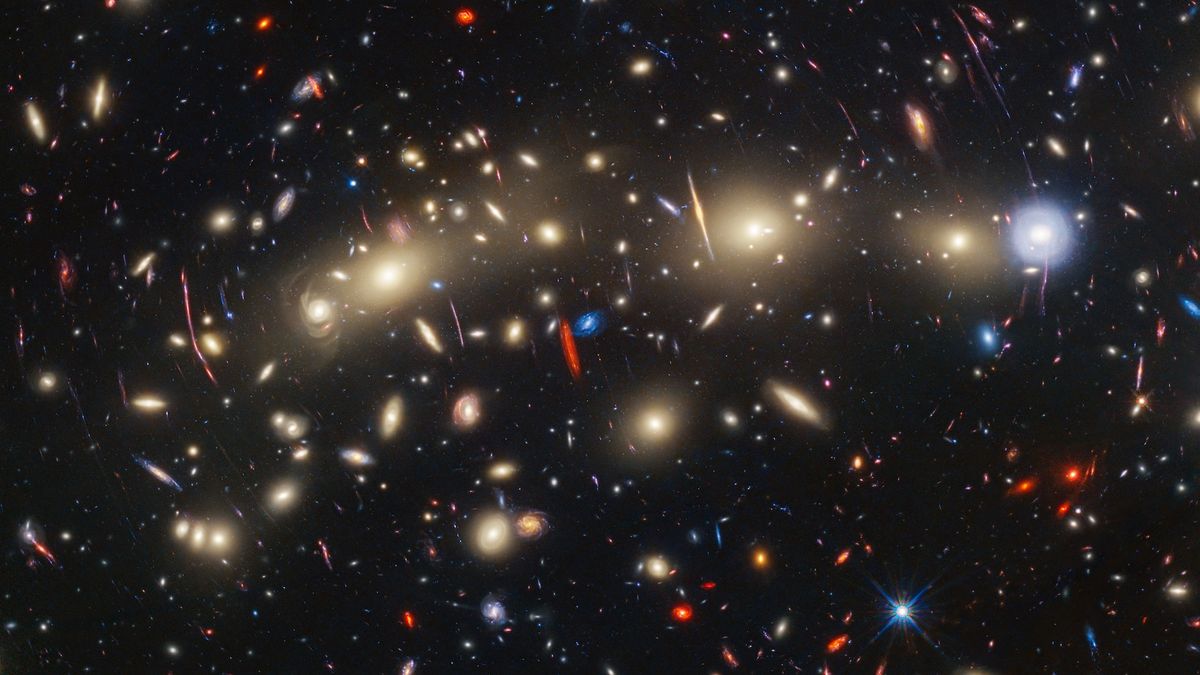
The Milky Way is just a speck in a universe filled with an untold number of galaxies. But if we had to take an educated guess, how many galaxies are in the universe?
That sounds like a simple question, but it’s anything but. The first problem is that even with our most powerful telescopes, we can see only a tiny fraction of the universe.
“The observable universe is only that part of the universe from which the light has had time to reach us,” astrophysicist Kai Noeske, now outreach officer at the European Space Agency, told Live Science.
The universe is 13.8 billion years old, but the observable universe stretches more than 13.8 light-years in every direction. That’s because the universe is expanding and light got a head start early on, when the universe was smaller.
“Now, the total size in each direction is about 46 billion light-years,” Noeske said.
That’s much smaller than even our smallest estimates of the entire universe. “We see at most 3% of the universe,” Pamela Gay, a senior scientist at the Planetary Science Institute, told Live Science.
Related: Why are galaxies different shapes?
The second problem is that there are so many galaxies that we can only make estimates of the total number based on what we can observe in small regions of the universe.
“You look at a small patch of the sky, and you count everything in that small patch and then multiply over the size of the sky,” Gay said.
But even that requires a cutoff. “What do we define [as] a galaxy?” Noeske said. “We have really giant galaxies that have to have a factor of 10 more” the mass of our galaxy, “and we have a lot of small galaxies, from lower-mass galaxies that have about 10 times less mass … down all the way to dwarf galaxies.”
At some point, scientists need to define a minimum mass for a galaxy to make estimates possible.
“If we set a mass cutoff and try to make this conservative, like a million solar masses, we end up with an average number of galaxies in the universe from the beginning to today of about 1 to 2 trillion,” Noeske said. Scientists think there were more galaxies earlier in the universe’s history than there are today, which is why galaxy estimates are an average over time.
“But those results come from the Hubble [telescope] — the James Webb Space Telescope is starting to speak to these results — which are near Earth, inside of our solar system, and are limited on what they can see by all the stuff in our solar system that adds light to the sky,” Gay said. “We do have one spacecraft with a camera that has gotten beyond all the garbage within our solar system, and that’s the New Horizons spacecraft.”
A 2021 study used the camera aboard New Horizons to measure the total amount of light in various patches of sky and estimated how many galaxies would be needed to create that much light.
“And suddenly, as they’re outside of all the light sources in our solar system, they realize we don’t need as many galaxies as we thought,” Gay said. “And so their estimates put us at, like, 200 billion, maybe even 100 billion galaxies in the visible universe.
“So somewhere between 2 trillion galaxies at the top edge and 100 billion at the lower edge is the number of galaxies in our observable universe,” she said.
If you assume that’s 3% — at most — of our universe, you can multiply that range of galaxies to get the total number of galaxies in the universe. If we’re seeing less of the universe than we think, there will be a smaller total number of galaxies.
But considering we don’t actually know the size of the universe, those estimates are murky. “If it’s an infinite universe, you’re going to have infinite galaxies,” Gay said.




















Discussion about this post