As the number of people conscious about their health increases, the search for alternatives to sugar is increasing. Jaggery, a traditional sweetener, has been gaining popularity as a healthier substitute. For people on a weight loss journey, jaggery is a joyful treat as they feel it would not hinder their progress. However, some are sceptical, thinking that since it is sweet, it might be just as harmful as processed sugar.
The consensus among those discussing weight loss is that sweeteners are a big no-no. Sugar, in any form, is often the first thing that gets crossed off the list. But is jaggery good for weight loss? It is a question that has been on the minds of many.
This article delves into the world of jaggery and its relationship with weight loss. We will explore the various forms of sugar, their effects on weight, and the benefits and precautions of consuming jaggery. Join us as we separate fact from fiction and discover whether jaggery can be a part of a successful weight loss diet.
Jaggery: An Overview
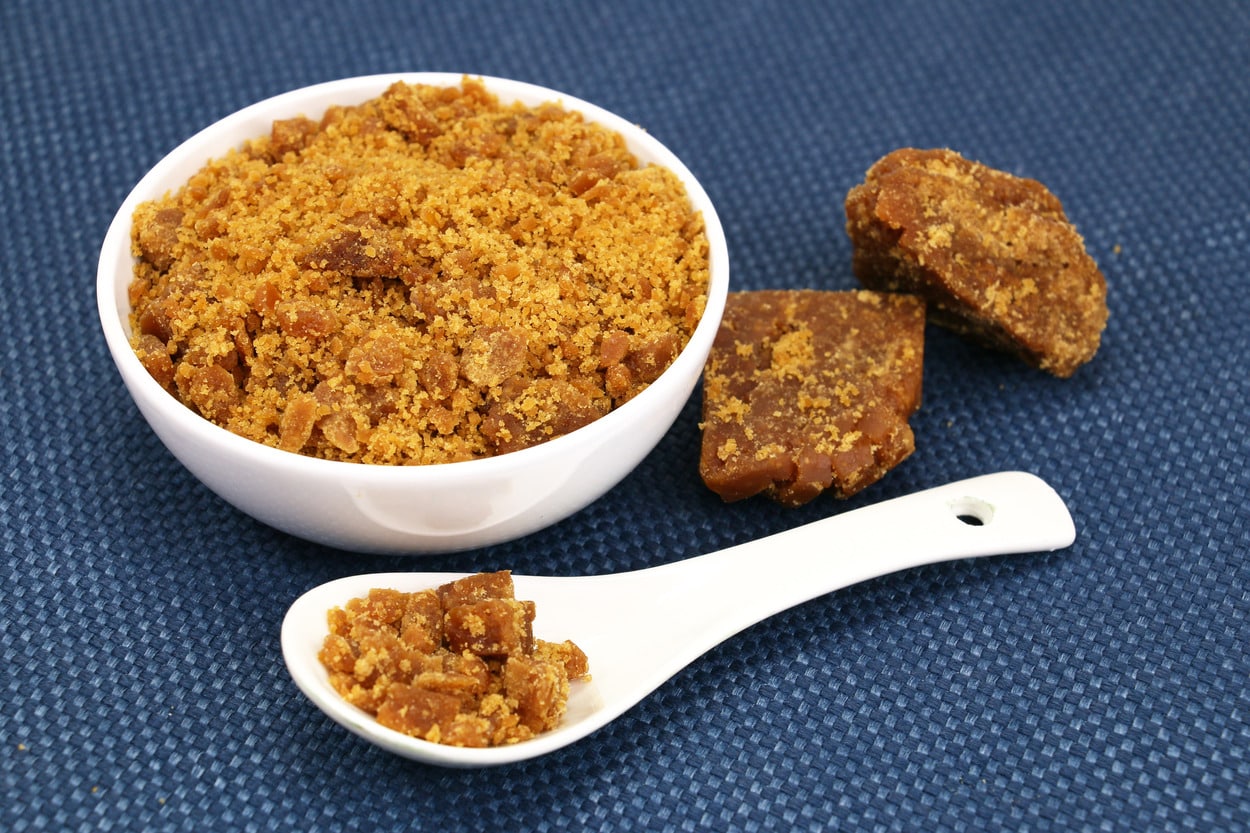
Jaggery, also known as ‘gur’, is a natural sweetener that people in Indian households have used for years. It is made by extracting the juice or sap from sugarcane, sugar beetroot, or date palms and cooking it for several hours until it thickens into a yellowish paste. During the process, manufacturers remove all contaminants to create a pure, unrefined sweetener that retains its high nutritional value.
Jaggery is not only known for its unique flavour but also for its health benefits. It is rich in antioxidants and minerals such as iron, calcium, and magnesium. These nutrients are often lost in the refining process of white and processed sugar, making jaggery a healthier alternative. In addition, due to its lower glycemic index, jaggery can also help regulate blood sugar levels, making it a suitable sweetener for individuals with diabetes.
Jaggery has gained popularity worldwide as a natural substitute for sugar. Some experts believe it can be a permissible addition to any weight loss diet. However, like any sweetener, one should consume it in moderation.
Nutritional Content of Jaggery
Research indicates that excessive consumption of refined sugars contributes to obesity, and thus it is essential to find healthier substitutes. Jaggery’s nutritional content suggests that it can be a healthy alternative.
Shalika’s Incredible Weight Loss Journey – Lost 38 kgs in 12 Months
Chat with us to get started on your health and fitness journey >> https://hlfy.me/YT_Video
As per USDA, one hundred grams of jaggery contains the following nutrients.
- Energy: 375kCal
- Carbohydrates: 100g
- Sugar: 100g
- Sodium: 250mg
- Calcium: 40-100 mg
- Vitamin B1: 0.01 mg
- Magnesium: 70-90 mg
- Potassium: 1056 mg
- Phosphorus: 20-90 mg
- Iron: 10-13 mg
- Vitamin C: 7.00 mg
- Manganese: 0.2-0.5 mg
- Zinc: 0.2-0.4 mg
Sugar and Weight Gain: The Connection
Sweeteners and added sugars enhance the flavour of various foods and beverages. Fructose, maize syrup and cane sugar are a few popular forms.
According to research, sugar is high in calories and lacks the essential vitamins, minerals, protein, fat, and fibre the body requires to operate optimally. Hence, added sugars get frequently referred to as ’empty calories.’
Foods and drinks like ice cream, candy, soda, and cookies which usually include a lot of added sugar, often have a high caloric content. Hence, one must avoid such food items or eat them rarely when looking to lose weight.
Summary
The connection between sugary foods and weight gain is well-known. Sugar adds as a form of empty calories. Although sugar may enhance the flavour of food, it leads to weight gain.
Types of Sugar
White Sugar
White sugar goes through various stages of processing. It loses most nutrients during the refining process. Most processing facilities employ sulphur to clean the sugar crystals of contaminants. The crystals frequently include trace amounts of sulphur. Over time, consuming them can be harmful to your health.
Moreover, research shows that the body ultimately gains fat due to white sugar consumption. It is because extra carbohydrates are metabolically transformed into fats by the liver. If not controlled, fats may build up in the liver, making it fatty. Related consequences are high blood pressure and diabetes.
Brown Sugar
Brown sugar gets its colour from molasses. As opposed to granulated white sugar, brown sugar has more flavour. It is a widely used ingredient in baked products since it has a rich sweetness. Since molasses absorb water, brown sugar and baked goods created with it keep their moisture well. Moreover, it is suitable for preparing sauces, marinades, and bacon.
If consumed in moderation, brown sugar is not as harmful. However, excessive use can raise the risk of diabetes, weight gain, and yeast infections.
Raw Sugar
Raw sugar, called turbinado or demerara sugar, is a less refined variety of sugar-containing residual natural molasses. It has a rougher texture and a darker colour than granulated sugar. Because of its distinctive flavour and undertones resembling caramel, raw sugar is used in sweetening coffee, tea, or mixed drinks. Compared to white sugar, it is more natural and less processed.
However, one must use raw sugar in moderation because it still has a similar caloric and carbohydrate content to other types of sugar.
Summary
Brown sugar, white sugar and raw sugar are the most common forms of sugar available. Although raw and brown sugar is relatively less harmful than white sugar, one must limit or avoid sugar consumption for weight loss.
Jaggery as a Substitute for Sugar: Is it Healthy?
Refined sugar is a commonly used sweetener in our diets. The blood quickly absorbs it, and hence it provides immediate energy. However, it also offers unnecessary calories and leads to an abrupt rise in blood sugar levels. Excessive consumption of refined sugar can cause weight gain and increase the risk of damaging vital organs, especially in people with diabetes.
Jaggery Over Sugar: Finding the Facts
Studies have shown that jaggery is a more suitable sugar substitute. Furthermore, some studies also show that jaggery offers various health benefits.
Jaggery comprises long chains of sucrose, a naturally occurring sweetening agent. Its high vitamin content aids digestion and provides health benefits. In addition, unlike refined sugar, the body slowly absorbs sucrose in jaggery, releasing energy over an extended period. As a result, it helps prolong the feeling of fullness, reduces hunger, and promotes weight loss.
Besides its sucrose content, jaggery is also an excellent source of potassium. Potassium supports electrolyte balance, increases metabolism, and strengthens muscles. Moreover, potassium helps in weight loss by lowering the water retained in the body. As some of our weight is a function of the water stored in our body, losing this water helps us lose weight, albeit temporarily.
Jaggery contains molasses, a syrup produced as a by-product of the sugar-making process. Molasses is thick, sweet, and brown and is removed chiefly from sugar during the refining process. Studies have shown that molasses contains various health benefits. Therefore, jaggery contains more nutritional elements than refined sugar available in the market.
Summary
Compared to sugar, jaggery contains some health benefits. One can use it as a replacement for sugar. The sweetness of jaggery comes from sucrose, a natural sweetening agent. It also has high potassium and vitamin content, making it a healthy sugar substitute. However, one should limit its consumption to moderation.
Incorporating Jaggery Into Your Diet
Using Jaggery as a Sweetener
Jaggery is an excellent substitute for refined sugar. One can sweeten milk, tea, coffee, and other drinks. One can add jaggery to many recipes to give them a distinctively sweet flavour. In addition to adding sweetness, it also offers several nutrients. However, it is still crucial to remember that it contains calories. Therefore, excessive consumption of jaggery as a sugar replacement is still unhealthy.
Pairing Jaggery with Nuts
Nuts and jaggery go well together as a food pairing. Jaggery can be added to roasted nuts like cashews, almonds, or peanuts to create a tasty and nutritious snack. Peanuts with jaggery coating or chana are popular on-the-go food items that leave you perked up.
Summary
Jaggery is a good substitute for refined sugar and can be used to sweeten drinks and recipes. It contains nutrients but should be consumed in moderation due to its calorie content. Jaggery can also be paired with nuts to make a tasty and nutritious snack.
Precautions
Jaggery is famous for its sweetness and dietary advantages. However, there are specific health concerns to be aware of. The first thing to remember is to watch how much you eat because jaggery still has a lot of calories and carbs. For people with diabetes, excessive consumption may result in weight gain or high blood sugar levels.
Additionally, buying jaggery from trustworthy vendors is vital to guarantee its quality and purity. Jaggery that has been contaminated or altered may be unhealthy.
Jaggery that has been contaminated or altered may be unhealthy. Not everyone should consume jaggery, particularly those with certain medical conditions or dietary prohibitions. Before introducing jaggery to your diet, speaking with your doctor or dietician is essential.
Summary
Jaggery has significant advantages for weight loss, but excessive consumption can harm your health and weight. So, remember to consume jaggery in moderation and as a part of a balanced diet to achieve your weight loss goals.
HealthifyMe Suggestions
Try replacing white sugar in your morning coffee or tea with jaggery. The natural sweetener will give your beverage a distinct, caramel-like flavour while providing several health benefits. Additionally, you can make jaggery granola by mixing rolled oats, nuts, seeds, and jaggery syrup and baking it in the oven. This crunchy and delicious granola can be a healthy snack or breakfast option, perfect for those on the go.
The Final Word
In conclusion, jaggery can be an excellent addition to your weight loss diet due to its lower glycemic index and ability to curb sugar cravings. However, it is essential to consume it in moderation, limiting intake to 1-2 tablespoons per day. Also, avoid combining jaggery with high-calorie foods and refrain from consuming jaggery-based desserts, as they are high in calories.
While jaggery is a healthier option than sugar, it is still a sweetener that contains calories and carbohydrates. Therefore, one must incorporate it into a balanced diet, regular exercise, and a healthy lifestyle to reap its potential benefits. So, enjoy jaggery, but do so in moderation and with caution.
Disclaimer: The purpose of this article is just to disperse knowledge and raise awareness. It does not intend to replace medical advice from professionals. For further information, please contact our certified nutritionists Here.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is jaggery?
A: Jaggery is a form of unprocessed sugar which goes by the name ‘Gur’. It is typically created by boiling raw, concentrated sugarcane juice until it solidifies. It can also be manufactured from coconut or date palm sap.
Q: Is jaggery good for weight loss?
A: Jaggery can aid in weight loss when included in a healthy, balanced diet and consumed in moderation. Compared to refined sugar, it is a natural sweetener with fewer calories and a lower glycemic index, which helps control blood sugar levels and prevents unexpected insulin spikes. Jaggery is also abundant in vital nutrients that help enhance energy levels and support general health when trying to lose weight.
Q: How does jaggery help in weight loss?
A: Due to its comparatively low-calorie content, lower glycemic index when compared to refined sugar, and the availability of vital elements that support overall health, jaggery can help people lose weight. It can be a natural substitute for processed sugars, helping regulate blood sugar levels, minimising unexpected insulin spikes, and helping people manage their weight.
Q: Can jaggery be a substitute for sugar while trying to lose weight?
A: Jaggery’s low calories, low glycemic index, and high nutritional value make it a healthier alternative to sugar when trying to lose weight. However, one should always consume it in moderation. Excess consumption can lead to adverse effects on your weight loss process.
Q: How much jaggery can one consume in a day for weight loss?
A: People have different limitations regarding the amount of jaggery to consume. It depends on their age, degree of activity, and daily calorie intake. To avoid consuming too many calories and to aid in weight loss, one should always consume jaggery in moderation, keeping daily intake to a teaspoon or less.
Q: Are there any side effects of consuming jaggery for weight loss?
A: Jaggery is typically harmless when used in moderation for weight loss. Yet, excessive consumption may result in weight gain due to its high-calorie content. In addition, people living with diabetes should keep an eye on their blood sugar levels because jaggery can raise or lower them.
Q: Can jaggery help in reducing belly fat?
A: While jaggery can be a healthier alternative to refined sugar, it alone is not proven to reduce belly fat specifically. Weight loss results from a balanced diet, regular exercise, and a healthy lifestyle. Including jaggery in moderation as part of an overall healthy eating plan may support weight loss efforts, but the targeted reduction of belly fat requires a comprehensive approach.
Q: Is jaggery better than honey for weight loss?
A: There is no clear answer to whether jaggery or honey is better for weight loss, as both contain calories and should be consumed in moderation as part of a healthy diet. However, jaggery is better than refined sugar as it contains some nutrients and has a lower glycemic index.
Q: Can jaggery be consumed by people with diabetes for weight loss?
A: Since jaggery contains natural sugar, those with diabetes should exercise caution while consuming it for weight loss because it may impact blood glucose levels. One should consult a healthcare professional or a registered nutritionist to assess the acceptability and safe use of jaggery for weight reduction for diabetes management.
Q: What are some healthy ways to consume jaggery while trying to lose weight?
A: Some healthy ways to consume jaggery while trying to lose weight include choosing jaggery-based sweets with lower calorie and fat contents, using it as a natural sweetener in beverages, desserts, or snacks in moderation, or combining it with nutrient-dense foods like nuts, seeds, or fruits for a balanced and healthy diet. Effective weight loss with jaggery depends on controlling calorie consumption and portion sizes.
Research Sources
1. Faruque S, Tong J, Lacmanovic V, Agbonghae C, Minaya DM, Czaja K. The Dose Makes the Poison: Sugar and Obesity in the United States – a Review. Pol J Food Nutr Sci. 2019;69(3):219-233. doi: 10.31883/pjfns/110735. PMID: 31938015; PMCID: PMC6959843.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6959843/
2. The U S Department of Agriculture
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/567640/nutrients
3. McGill AT. The sugar debate and nutrition: obesity and ’empty calories’. N Z Med J. 2014 Apr 11;127(1392):6-11. PMID: 24806242.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24806242/
4. Stanhope KL. Sugar consumption, metabolic disease and obesity: The state of the controversy. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2016;53(1):52-67. doi: 10.3109/10408363.2015.1084990. Epub 2015 Sep 17. PMID: 26376619; PMCID: PMC4822166.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4822166/
5. Kumar, Abhai & Singh, Smita. (2020). The benefit of Indian jaggery over sugar on human health. 10.1016/B978-0-12-816918-6.00016-0.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/339908838_The_benefit_of_Indian_jaggery_over_sugar_on_human_health
6. Hirpara, Parth & Thakare, Nitin & Kele, Vijay & Patel, Dhruvin. (2020). Jaggery: A natural sweetener. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry. 9. 3145-3148.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/344921769_Jaggery_A_natural_sweetener
7. Rahiman F, Pool EJ. The effect of sugar cane molasses on the immune and male reproductive systems using in vitro and in vivo methods. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2016 Oct;19(10):1125-1130. PMID: 27872709; PMCID: PMC5110661.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5110661/




















Discussion about this post