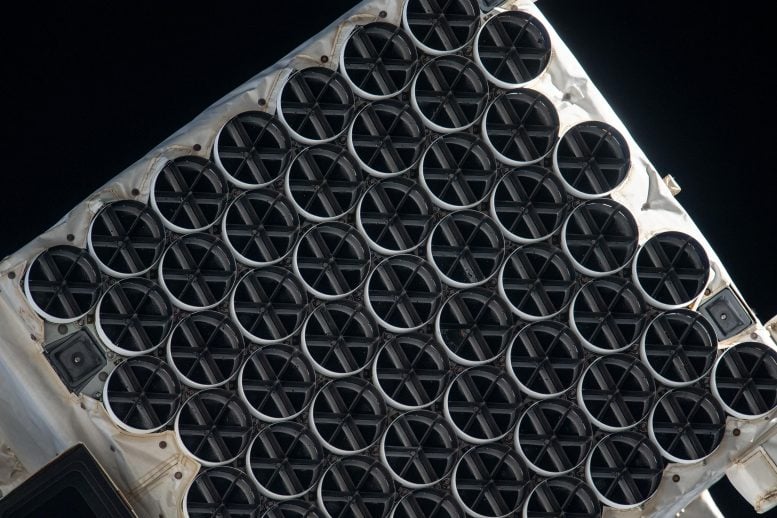
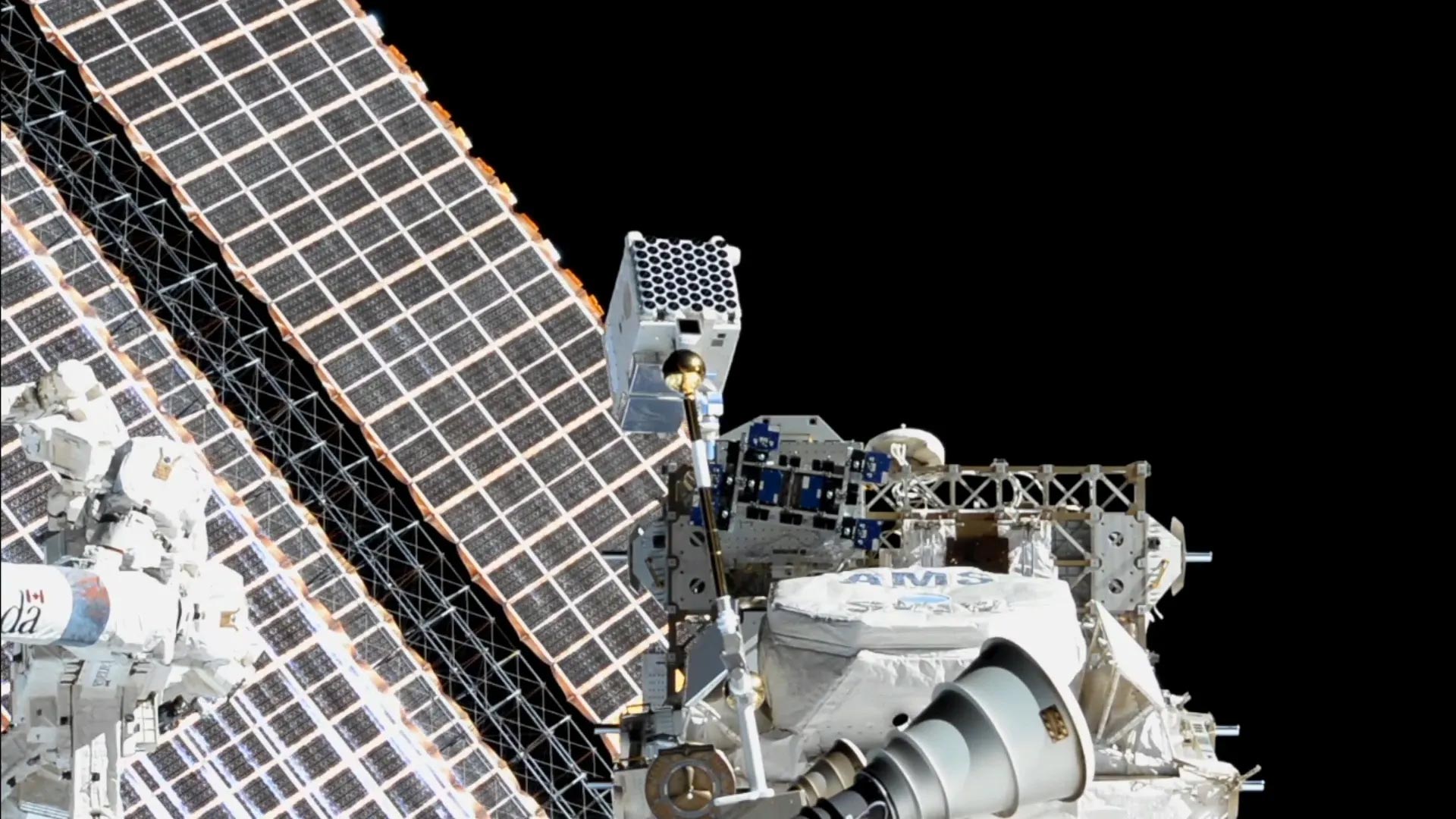
This image, obtained June 8, 2018, shows NASA’s NICER (Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer) on the International Space Station, where it studies neutron stars and other X-ray sources. NICER is about the size of a washing machine. The sunshades of its X-ray concentrators are visible as an array of circular features. Credit: NASA
NASA is set to repair the NICER telescope on the ISS with a specially designed patch kit during a spacewalk.
The telescope, crucial for studying neutron stars and X-ray phenomena, was damaged in May 2023, leading to a rapid design and testing of a solution. The upcoming mission will make NICER the first X-ray telescope serviced by astronauts, enhancing its ability to conduct groundbreaking science.
UAE (United Arab Emirates) astronaut Sultan Alneyadi captured this view of NICER from a window in the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 on the space station in July 2023. Photos like this one helped the mission team map the damage to the thermal shields over NICER’s X-ray concentrators. Credit: NASA/Sultan Alneyadi
NICER Telescope Repair
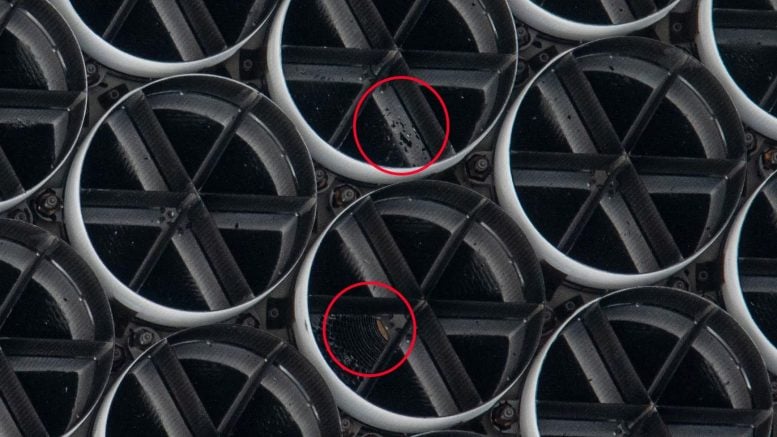

Some of NICER’s damaged thermal shields (circled) are visible in this photograph. Credit: NASA/Sultan Alneyadi
Rapid Response and Innovation
“It’s incredible that in just one year, we were able to diagnose the problem and then design, build, test, and deliver a solution,” said Steve Kenyon, NICER’s mechanical lead at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. “We’re so excited to see the patches installed during a future spacewalk, return to a more regular operating schedule, and keep doing groundbreaking science.”
From its perch on the station, the washing machine-sized NICER studies the X-ray sky. It has precisely measured superdense stellar remnants called neutron stars, which contain the densest matter scientists can directly observe. It has also investigated mysterious fast radio bursts, observed comets in our solar system, and collected data about Earth’s upper atmosphere.
But in May 2023, NICER developed a “light leak,” where unwanted sunlight began entering the telescope.
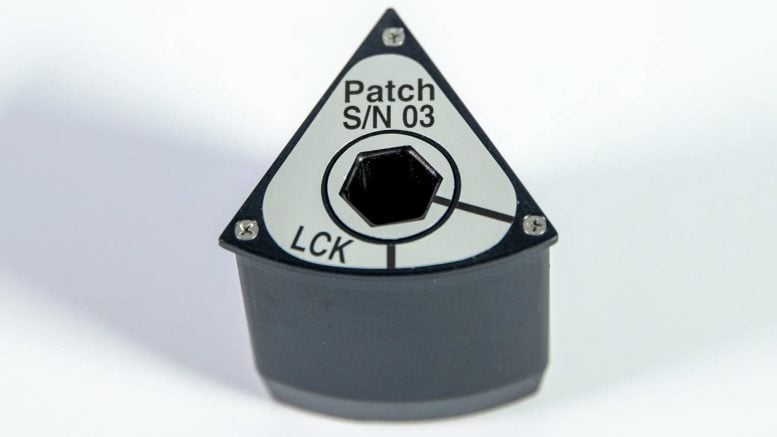

NICER’s patches are made from aluminum and anodized, or coated, black. Each is about 2 inches tall. “LCK” indicates the lock position for a tab at the bottom that will hold the patch in place. NASA is sending 12 of these patches to the International Space Station. During a spacewalk, astronauts will insert five into sunshades on the telescope to cover the most significant areas of damage. Credit: NASA/Sophia Roberts
Photos taken aboard the station revealed several areas of damage to NICER’s thermal shields. The shields are 500 times thinner than a human hair and filter out infrared, ultraviolet, and visible light while allowing X-rays to pass through. They cover each of NICER’s 56 X-ray concentrators, sets of 24 nested circular mirrors designed to skip X-rays into corresponding detectors. A sunshade tops each concentrator and shield assembly, with a slight gap in between. The sunshades are segmented by six internal struts, resembling a sliced pie.
The largest damage to the shields is around the size of a typical U.S. postage stamp. The other areas are closer in size to pinheads. During the station’s daytime, the damage allows sunlight to reach the detectors, saturating sensors and interfering with NICER’s measurements. The mission team altered their daytime observing strategy to mitigate the effect. The damage does not impact nighttime observations.
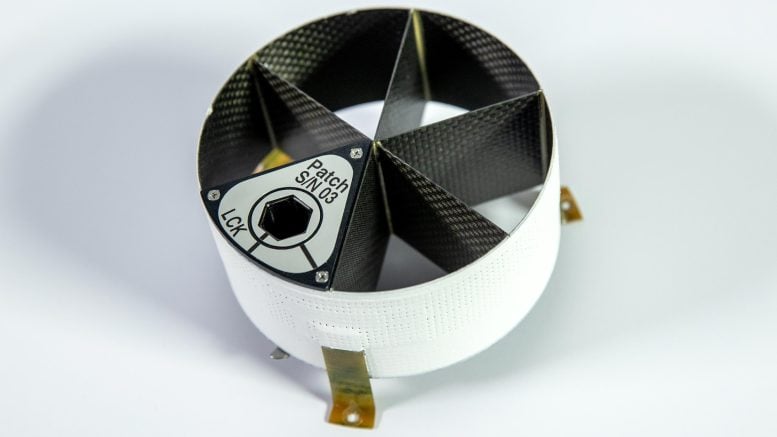

NICER’s patches will be inserted into its sunshades, as shown here. The small tab that locks the patch into place is visible beneath it. The carbon composite sunshades cover each of NICER’s 56 X-ray concentrators. Each sunshade is supported by three gold-colored fiberglass mounting feet. Credit: NASA/Sophia Roberts
Technical Challenges and Solutions
“NICER wasn’t designed to be serviced or repaired,” said Keith Gendreau, the mission’s principal investigator at Goddard. “It was installed robotically, and we operate it remotely. When we decided to investigate the possibility of patching the largest damaged areas on the thermal shields, we had to come up with a method that would use the existing parts of the telescope and station toolkits. We couldn’t have done it without all the support and collaboration from our colleagues at Johnson and throughout the space station program.”
The solution, in the end, was simple. The team designed patches, each shaped like a piece of pie, that will slide into the sunshades. A tab at the bottom of each patch will turn into the space between the bottom of the sunshade and the top of the thermal shield, keeping it in place.
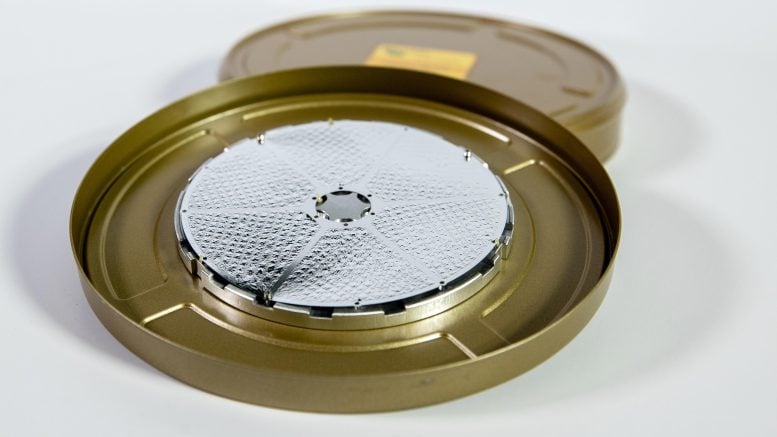

NICER’s thermal shields — the silver film shown here — cover each of the mission’s 56 X-ray concentrators. They block ultraviolet, infrared, and visible light while allowing X-rays to pass through to the mirrors underneath. Each shield is only about 160 nanometers thick, or 500 times thinner than a human hair. The fragile shield is supported by a stainless-steel frame which consists of a pattern of 1/8 inch (3 millimeter) squares in each of the wedges. Credit: NASA/Sophia Roberts
Upcoming Spacewalk and Future Expectations
Astronauts will install five patches during the spacewalk. They’ll cover the most significant areas of damage and block the sunlight affecting NICER’s X-ray measurements.
The repair kit contains 12 patches in total, allowing for spares if needed. Astronauts will carry the patches in a caddy, a rectangular frame containing two spare sunshades with the patches held inside.
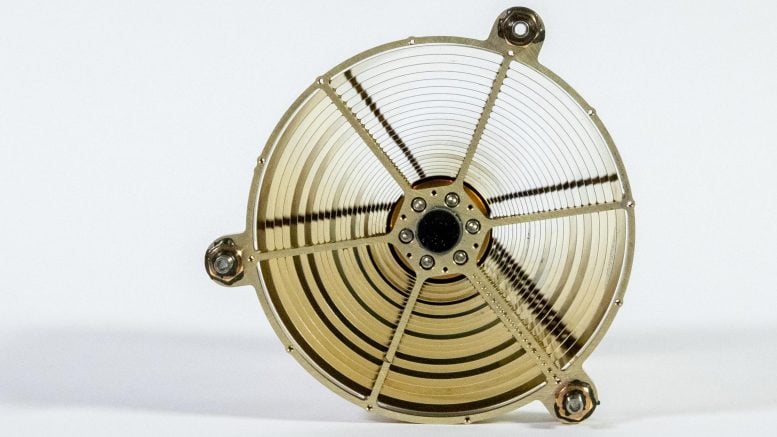

NICER has 56 individual X-ray focusing elements, called concentrators, that each contain 24 nested mirrors. Every concentrator delivers X-rays to its own detector. The concentrator shown here is tilted on its side, so the camera is looking into the nested mirrors. X-rays are high-energy light, so they can pass through the atoms of telescope mirrors like those for NASA’s Hubble and James Webb space telescopes. Instead, X-ray observatories use grazing incidence mirrors, where the surfaces are turned on their sides. X-rays skip across their surfaces and into detectors. Credit: NASA/Sophia Roberts
“NICER will be the first X-ray telescope in orbit to be serviced by astronauts and only the fourth science observatory to be repaired overall — joining the ranks of missions like NASA’s 
The NICER caddy is an aluminum box containing two of the mission’s spare sunshades, which are attached to the bottom. Inside the sunshades, 12 patches are locked into place. Astronauts will take the complete caddy assembly with them during a future spacewalk to address damage to NICER’s thermal shields. They’ll insert five of the patches over the largest areas of damage, which will allow the mission to return to a normal operating status during the station’s daytime. Credit: NASA/Sophia Roberts
The Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) is an X-ray astronomy instrument on the International Space Station (ISS), focused on studying neutron stars, including pulsars. Part of NASA’s Explorers Program, NICER aims to measure the extreme physical properties of neutron stars to advance our understanding of their dense interiors. It also supports the SEXTANT experiment, which tests




















Discussion about this post