NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory captured this image of a solar flare — seen as the bright flash on the right — on Aug. 5, 2024. The image shows a subset of extreme ultraviolet light that highlights the extremely hot material in flares and which is colorized in teal. Credit: NASA/SDO
On August 5, 2024, 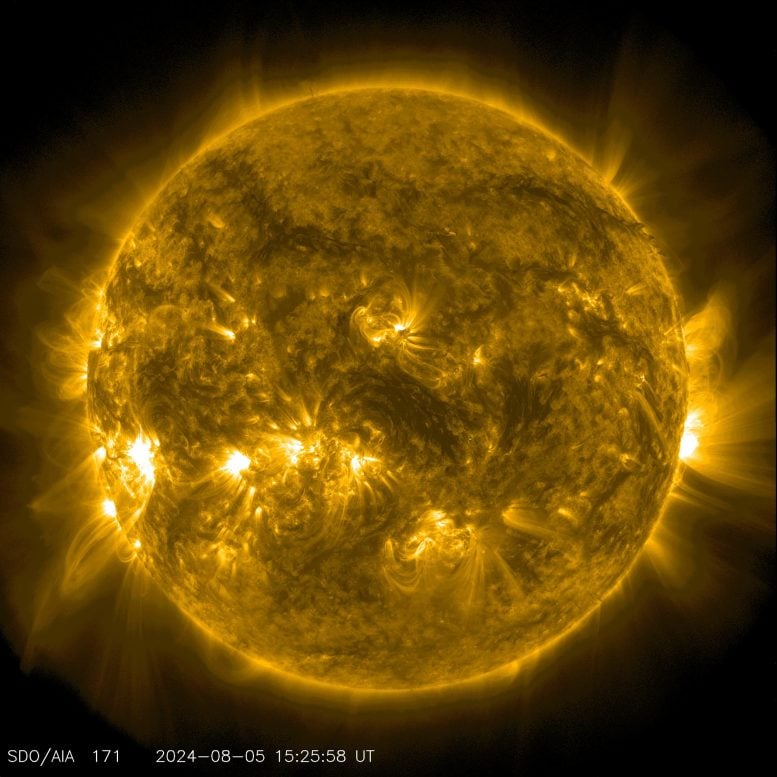
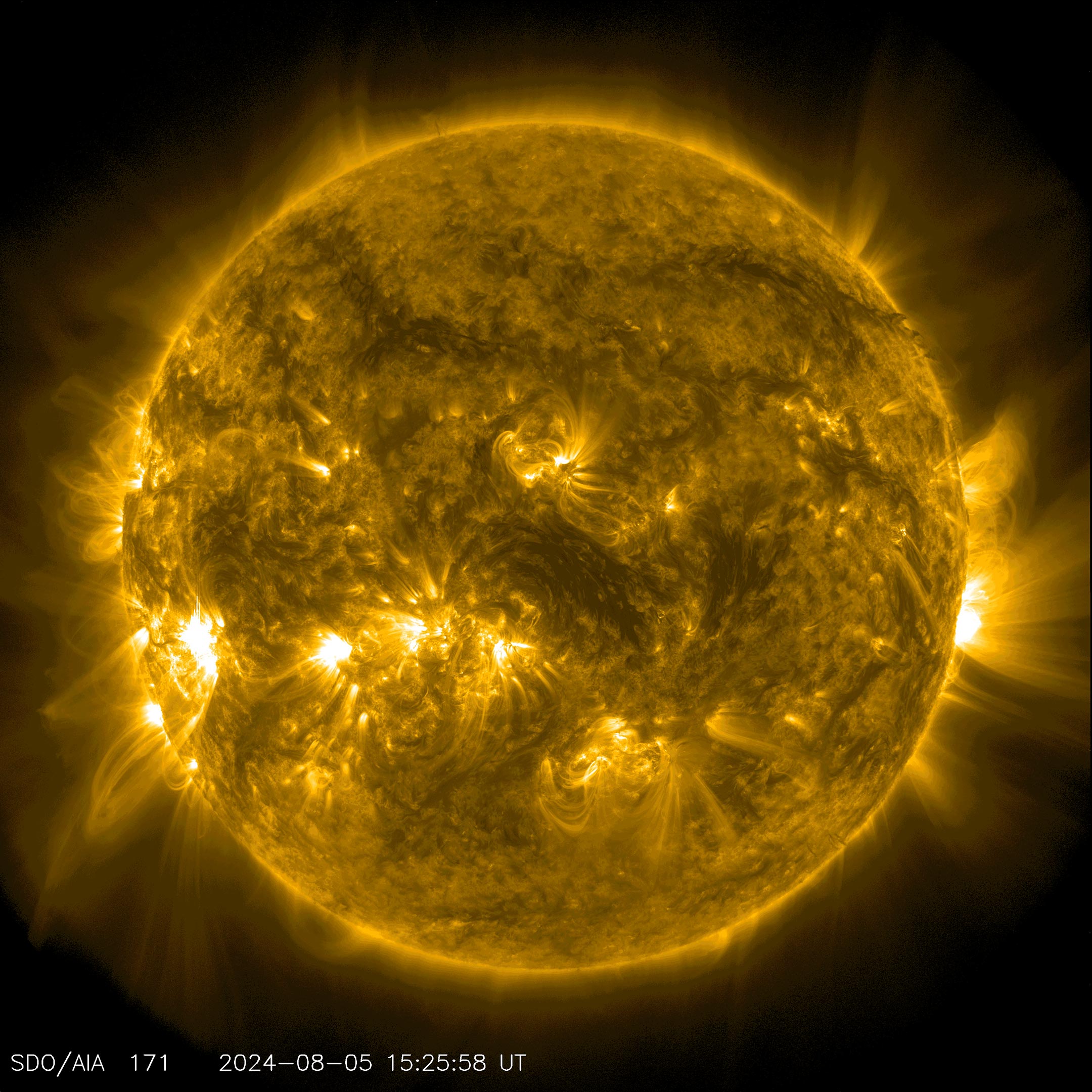
NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory captured this image of a solar flare — seen as the bright flash on the lower left – on Aug. 5, 2024. The image shows a subset of extreme ultraviolet light that highlights the extremely hot material in flares and which is colorized in gold. Credit: NASA/SDO
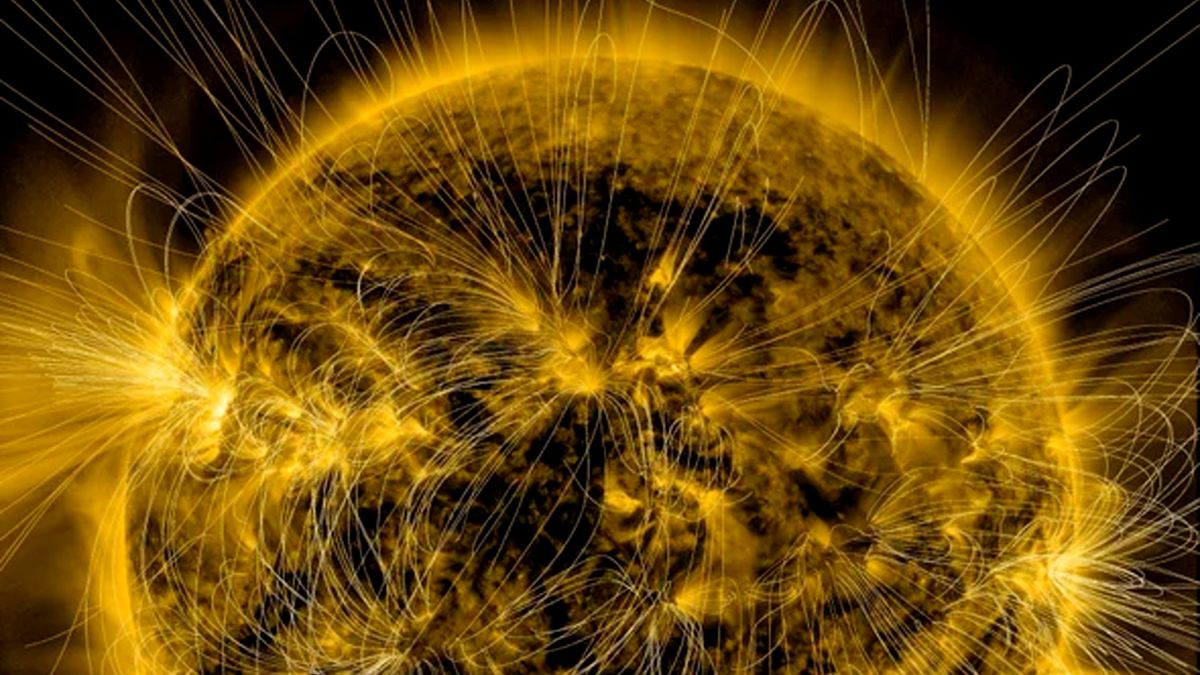
Solar flares are intense bursts of radiation emanating from the release of magnetic energy associated with sunspots. They are the most powerful kind of solar phenomena and can last from minutes to hours. Flares are often categorized by their strength, from Class A (the weakest) to Class X (the strongest), with each class having a finer scale from 1 to 9.
When solar flares occur, they emit energy across the entire electromagnetic spectrum—from radio waves to gamma rays. Although these bursts of energy are primarily emitted into space, when directed towards Earth, they can have profound effects on the upper atmosphere, causing disruptions in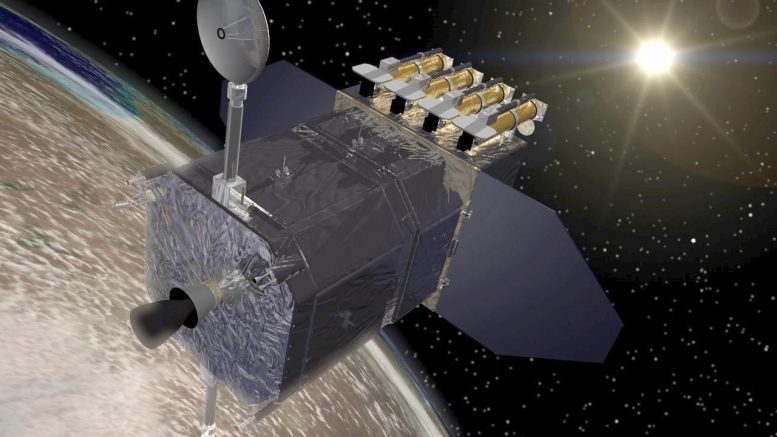 
Artist’s concept of the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Credit: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Conceptual Image Lab
Launched in 2010, NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) is a key player in space weather research, keeping a vigilant eye on the Sun’s activity from its geosynchronous orbit above Earth. The SDO’s mission is to unravel the mysteries of solar variability and its impacts on our planet.
Armed with advanced instruments like the Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) and the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA), SDO captures high-resolution images of the Sun in multiple wavelengths, revealing the hidden mechanics of solar flares and coronal mass ejections. These insights help forecast space weather events that can disrupt satellite operations, communications, and power grids on Earth, making SDO an essential tool for understanding and mitigating solar threats.




















Discussion about this post