Recent research illuminates the complex dietary strategies of desert isopods, showing how they balance nutrient intake and rely on environmental microorganisms to optimize digestion and growth. Credit: Moshe Zaguri
New insights into the dietary habits of desert isopods unveil the multifaceted elements guiding their food selection. The study reveals that these creatures carefully balance their nutrient intake, favoring biological soil crusts over plant litter, which illuminates the complex web of trophic interactions. By examining the specific eating patterns of desert isopods, this research enhances our comprehension of the delicate relationships among organisms and their habitats, providing valuable implications for ecosystem management and conservation efforts.
A new study published in Ecology Letters illuminates the intricate nutritional and functional dynamics influencing the dietary choices of desert isopods (Hemilepistus reaumuri). The research, led by Prof. Dror Hawlena from the Hebrew University’s Institute of Life Sciences and conducted by Dr. Moshe Zaguri (formerly a Ph.D. student at the Hebrew University, now at the Volcani Institute) in collaboration with Prof. David Raubenheimer from the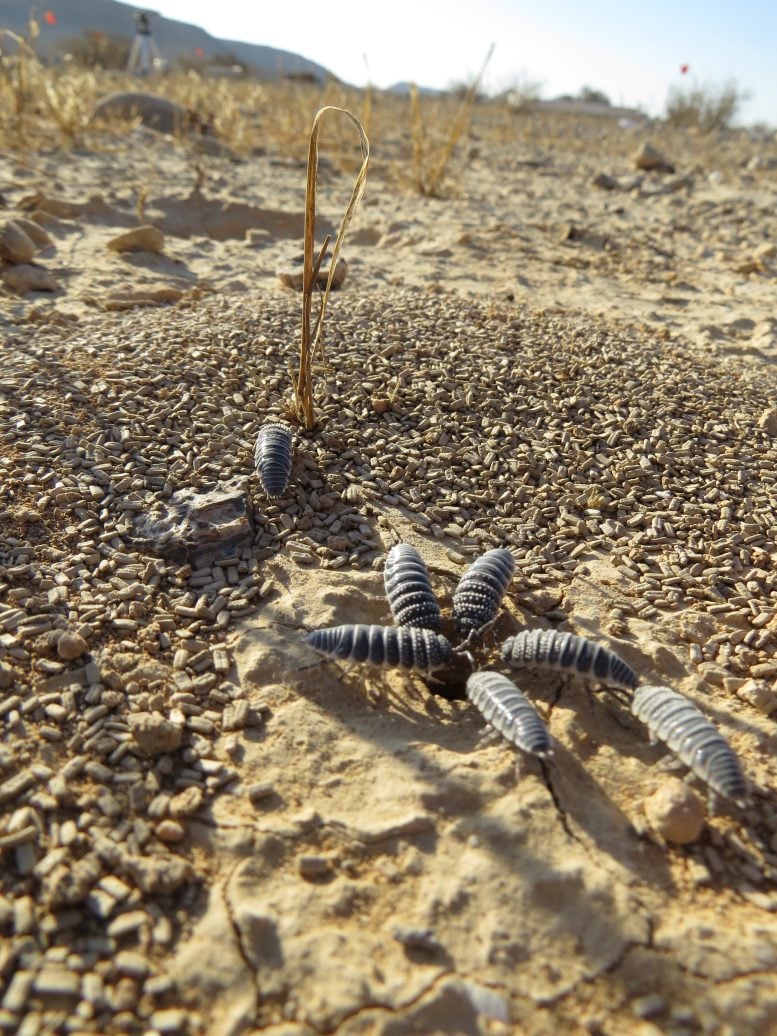 
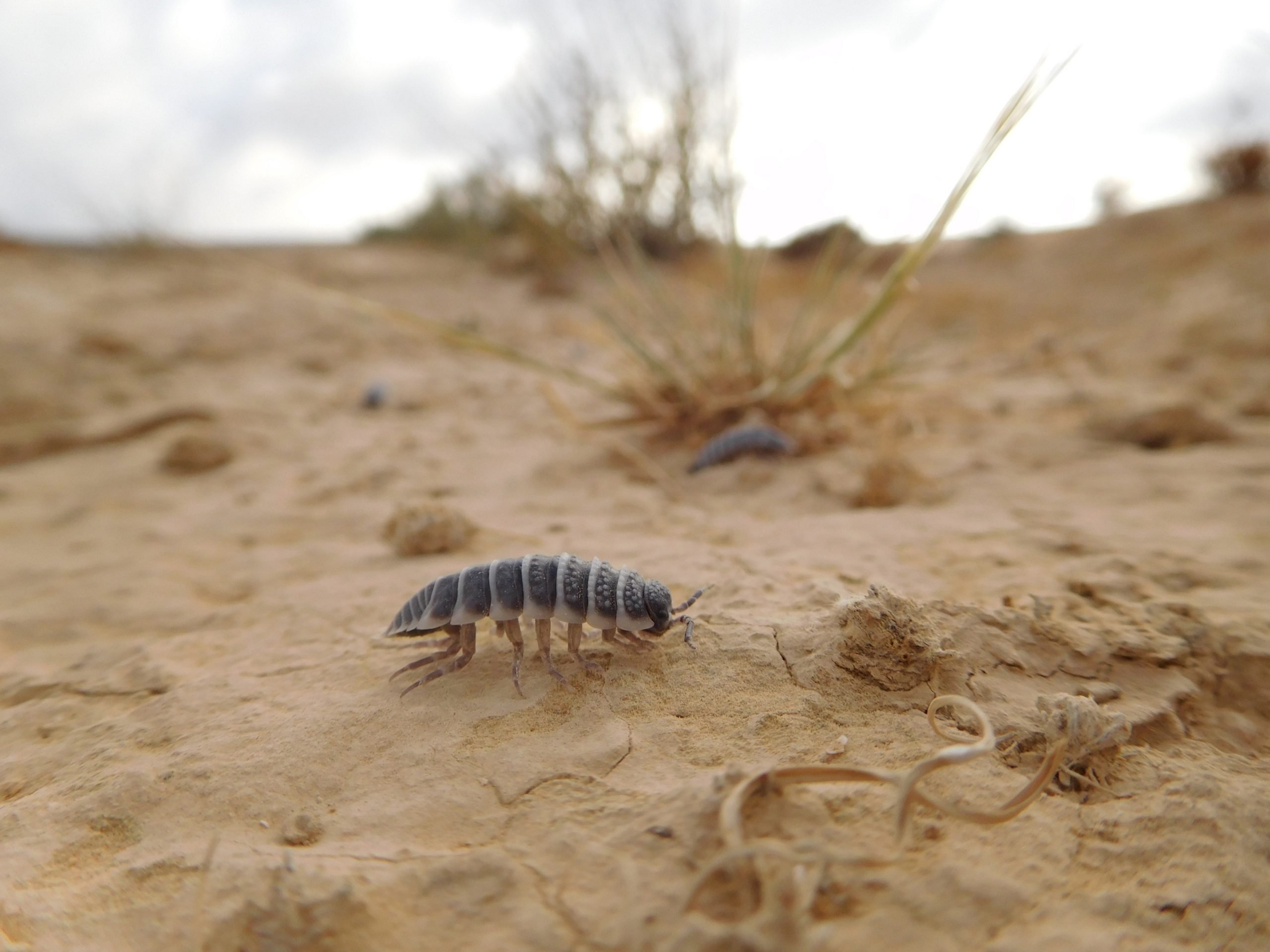
Isopod siblings start the day by cleaning the burrow before foraging. Credit: Moshe Zaguri
The researcher fed isopods with natural and artificial foods and found that when allowing a choice, isopods can tightly regulate their food consumption to meet a very specific ratio of proteins, sugars, and calcium. Isopods receive most of their proteins and sugars from dry leaves and eat soil crust to meet their very high calcium needs. The exoskeleton of isopods is made of calcium carbonates that they must consume in large quantities to grow.
However, when isopods could supplement leaf litter with artificial sources of calcium, they successfully met their exact calcium needs, but suffered reduced growth. The authors used gamma-radiation to kill the microorganisms of the soil crust while maintaining its nutritional value and measured the isopods’ food assimilation efficiency and growth rate in comparison to isopods that ate the untreated crust. The authors found that isopods eat the crust to incorporate live microorganisms to their digestive system. Those microbes assist in improving the digestion of the fibrous plant litter. The authors concluded that isopods eat foods that allow them to meet their nutritional needs by providing the nutrients but also by helping them to digest. These revolutionary findings may shed new light on how different animals and humans choose their diet by considering both the foods’ nutrients and the existence of digestive assisting agents. Humans do not eat soil crust but may think about the general insights of this interesting study during their next visit to the local grocery shop.
Insights into Isopod Dietary Preferences and Nutrient Optimization
Animals optimize their fitness by assimilating specific quantities and ratios of macronutrients and mineral nutrients. To understand this phenomenon, the team conducted extensive field and laboratory experiments focusing on the dietary preferences of desert isopods. Contrary to expectations, wild isopods exhibited a preference for macronutrient-poor biological soil crust (BSC) over plant litter, consuming three times more of the former.
The research revealed that desert isopods rigorously regulate their intake of macronutrients and calcium, with phosphorus intake remaining unaffected. Moreover, the team observed that despite equivalent calcium ingestion, isopods thrived better when consuming BSC compared to artificial foods. Notably, isopods consuming gamma-radiation-sterilized BSC exhibited increased consumption but slower growth rates compared to those consuming live BSC, suggesting the crucial role of ingested microorganisms in facilitating litter digestion.
Dr. Moshe Zaguri, lead researcher of the study, commented, “Our findings underscore the complexity of dietary decision-making among desert isopods and highlight the importance of considering multifaceted factors in understanding trophic interactions.”
Understanding the complex nutritional and functional considerations driving the dietary choices of desert isopods is crucial for advancing our knowledge of ecological dynamics. This research sheds light on how these animals optimize their fitness by regulating nutrient intake and preferring specific food sources. By uncovering the role of ingested microorganisms in facilitating digestion and growth, the study emphasizes the interconnectedness of organisms and their environment. Moreover, it highlights the broader implications for ecosystem management and conservation efforts, underscoring the need for interdisciplinary approaches in ecological research to address the multifaceted factors influencing trophic interactions and ecosystem functioning.
Reference: “‘Dust you shall eat’: The complex nutritional and functional considerations underlying a simple diet” by Moshe Zaguri, Irit Mogilevsky, David Raubenheimer and Dror Hawlena, 15 April 2024, Ecology Letters.
DOI: 10.1111/ele.14414




















Discussion about this post