The ocean-facing edge of a glacier in Greenland. A research expedition led by The University of Texas at Austin is about to conduct the first-ever robotic survey of these glaciers from underwater. Credit: European Space Agency
A team from the University of Texas is conducting a groundbreaking study on Greenland’s glaciers to understand the underwater mechanisms of glacier melting and the role of sediments in slowing this process. Their findings will provide insights into future sea level rises, essential for preparing coastal communities globally.
A team of scientists from the University of Texas at Austin have embarked on a four-week expedition to explore the underwater edges of Greenland’s coastal glaciers to learn more about future sea level rise. In collaboration with international partners, the scientists will investigate processes that control how these giant glaciers melt and what that means for the future of the Greenland ice sheet, which has about 23 feet (7 meters) of potential sea level rise locked away in its ice.
Joining the researchers is a robotic submersible that will gather measurements of the glaciers’ underwater walls and sediment-laden meltwater, a feat that’s never been attempted up close. The scientists will also conduct extensive surveys of the seafloor and gather sediment cores that will let them wind back the clock to see how past periods of climate change affected glaciers.
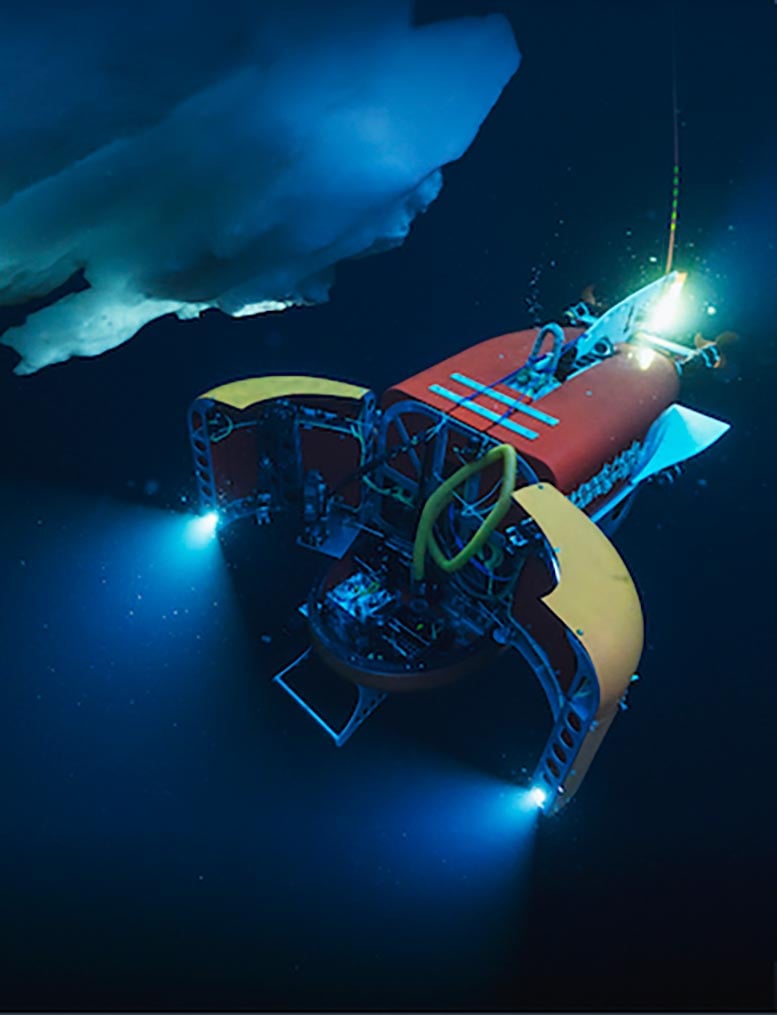

Nereid Under Ice (NUI), a robot submersible developed and operated by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, during a 2019 expedition in the Arctic Ocean. The UT Austin-led mission will rely on the vehicle’s ability to operate in the difficult conditions near Greenland’s large glaciers. Credit: Luis Lamar, courtesy of the Avatar Alliance Foundation
Understanding Sediments and Glacial Stability
A key research question is the role of sediments in slowing glacial melt, said the expedition’s chief scientist Ginny Catania, a research professor at the University of Texas Institute for Geophysics (UTIG) and UT’s Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences. UTIG is leading the expedition and is part of the UT Jackson School of Geosciences.
“Most of the ice sheet has retreated, but there are a few glaciers that have not retreated next to glaciers that have retreated a lot. And it could be because sediments are stabilizing the glaciers,” Catania said.
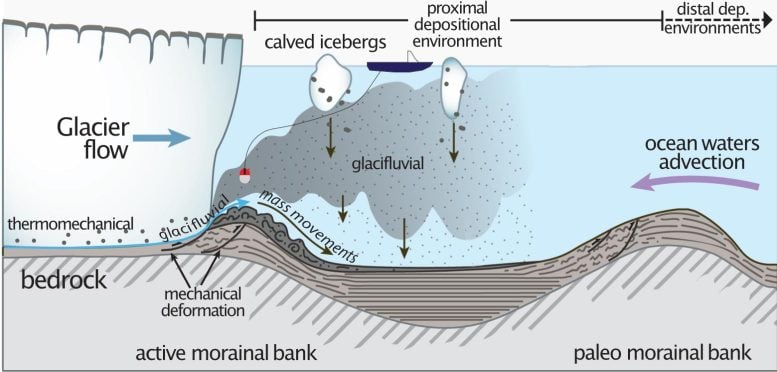
A graphic showing how sediments from under the glacier pile up into buttressing moraines and how the UT Austin-led expedition plans to explore the glacial environment. Credit: Ginny Catania
The researchers think that the glaciers are protected from warm ocean currents by underwater walls, called moraines, that pile up from sediment carried from beneath the glacier itself. These buttressing walls also form when glaciers advance, bulldozing the seafloor ahead of them.
But how effective are they at slowing melt, how quickly do they form, and how long do they persist? Answering those questions should give scientists a much better idea of the future of the ice sheet both in Greenland and Antarctica, where sediment may also play a role in stabilizing glaciers. These answers, in turn, can help with predicting how quickly the sea level will rise in the coming years.
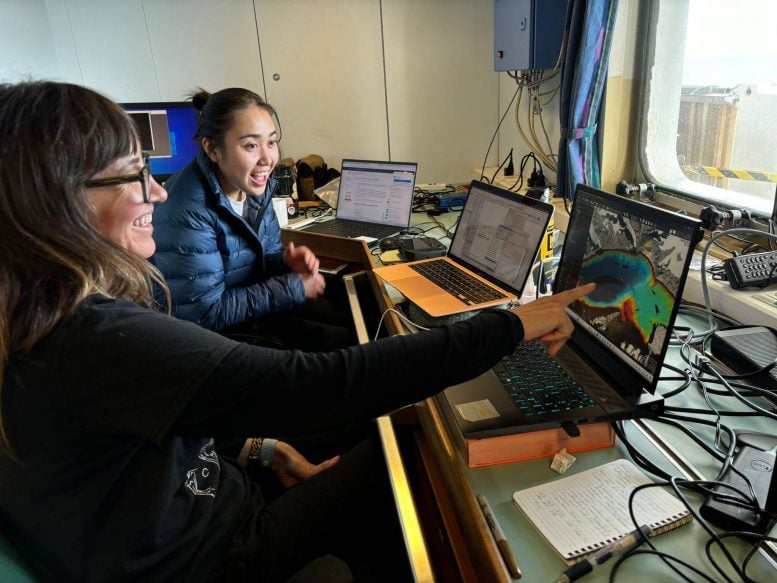

Chief scientist Ginny Catania and Jackson School graduate student Casey Vigilia examine preliminary bathymetry data of the expedition’s first target, the glacier Kangerdlussauq, while en route to the study area. Credit: Marcy Davis/University of Texas Institute for Geophysics
Advanced Technologies and Data Collection
Catania explained: “This is a big mission to try to capture as much information about how the glaciers behave underwater with these really sophisticated tools that we haven’t been able to use in the past.”
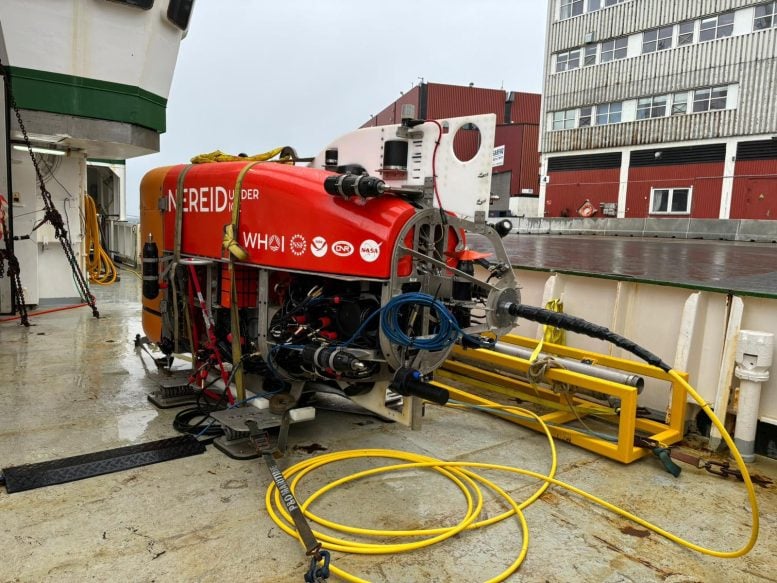

NUI awaits deployment on the deck of the research vessel Celtic Explorer. The robot submersible’s first survey target is Kangerdlussauq, a large glacier in West Greenland. Credit: Marcy Davis/University of Texas Institute for Geophysics
The robotic submersible Nereid Under Ice (NUI) is key to collecting the data that can answer these questions. NUI was developed and is operated by engineers at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, who are on board for the mission. It is specially designed to navigate the treacherous, icy environment of the glacial fjord, where it will use its sensors and samplers to measure sediments flowing out from under the ice and to conduct unprecedented, up-close geophysical surveys of the ice and seafloor.
Similar measurements will be made by an XOcean sea surface drone and larger instruments aboard the expedition’s vessel, the Marine Institute of Ireland’s RV Celtic Explorer. Researchers will also gather data from the glaciers’ surface using aerial drones.
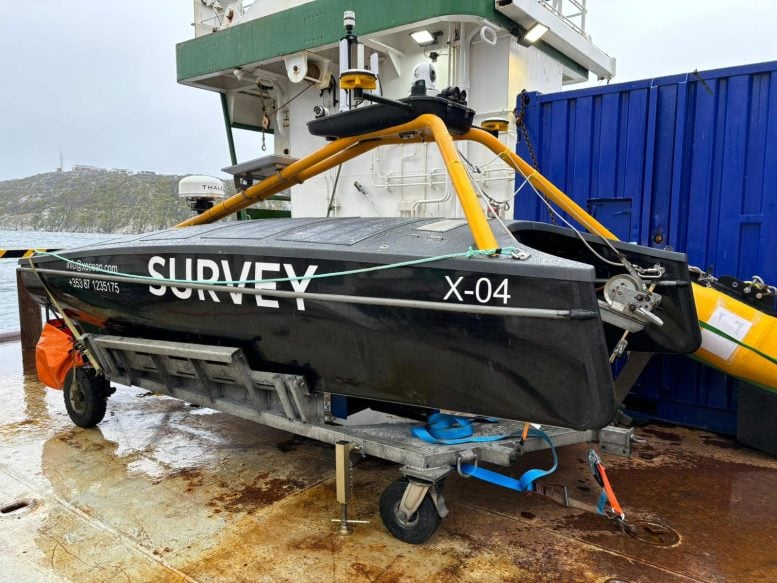

A sea surface drone supplied by XOcean. Researchers will remotely pilot the drone through ice fields to the glacier’s towering face where it will conduct high-resolution scans of the seafloor and sediment walls, called moraines. Credit: Marcy Davis/University of Texas Institute for Geophysics
Implications for Coastal Communities
What the expedition reveals about future sea level rise will be vital for coastal communities around the world, said Catania, who also leads a Texas coastal research effort. “A lot of the research needs to be in understanding how the coast is going to respond to this inundation and what governments can do about it,” she said.
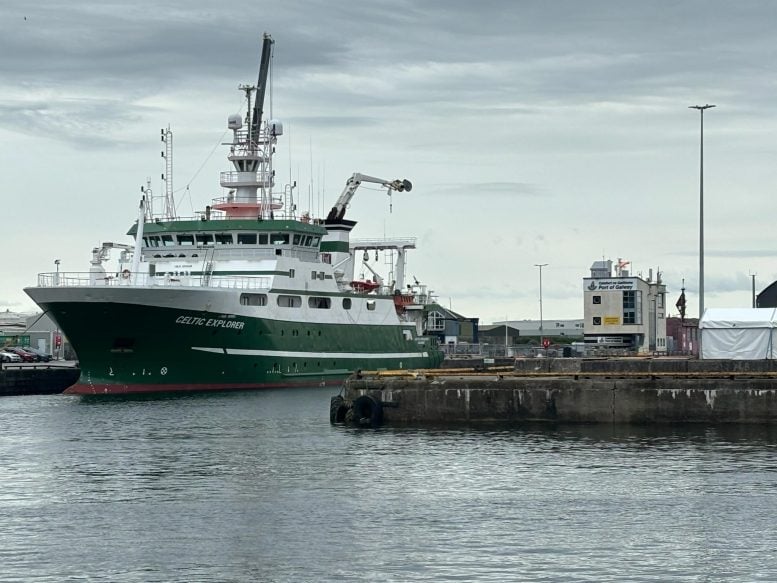

The Marine Institute’s research vessel, Celtic Explorer, prepares to depart for Greenland. The UT Austin-led expedition will conduct surveys of glacial walls using the vessel’s instruments alongside a robotic submersible, sea, and aerial drones. Credit: Sean Gulick/Jackson School of Geosciences
Collaborative Research Effort
Catania’s expedition team is made up of 24 researchers, engineers, and students from seven institutions, including UT, Woods Hole,



















Discussion about this post