Cloud-based app development uses features from cloud platforms to build scalable applications using Google cloud services over the Internet. Serverless architecture is a cloud-based code execution model where the cloud provider handles all the backend resources.
Serverless computing is on the rise, with businesses extensively demanding it. It has been stated that more than 50% of companies will switch to serverless architecture by 2025.
How serverless architecture works
It is defined as a model where a third party handles all the servers and backend, which includes databases, security, storage, etc. The company does not have to deal with any infrastructure, which enables them to focus on other integral parts. Enterprises develop as well as deploy their applications on a server hosted by a third party, which handles all the logistics and backend support. The service provider, such as AWS, Google, and IBM, take all the management and maintenance. Serverless architecture is also sometimes referred to as “function-as-a-service.”
Serverless computing is only charged when used, usually triggered by some event. It depends on the operation, the time it takes, the number of resources it’s using, the amount of code that must be run, etc. It does not have a monthly/yearly fee and is also purely based on the actions triggered by any request.
The customer has to develop the business logic and write the code, which is then uploaded. The provider then takes care of the rest, i.e., hardware management, processes like multi-threading, allocation of virtual machines, etc.
No wonder this model is in such demand as it reduces the technical load on the client by tons and helps to make efficient, quick, as well as scalable applications!
Understanding serverless architecture better
There are a few terms that one must keep in mind to understand serverless architecture better:
- Backend as a service: Cloud service model that involves outsourcing all the backend of an application, which handles tasks like cloud storage, authentication, etc.
- Container: It’s an abstraction layer that packages code and its dependencies. Multiple containers can be run together; it helps to promote isolation.
- Event-driven architecture: This type of architecture uses events to set off a trigger, enabling communication between the microservices.
- Cold start: In serverless architecture, it refers to the latency or time delay when a function is first triggered or triggered after a long period of inactivity.
- Concurrency limit: The number of function instances that can run simultaneously in a region pre-decided by the cloud provider.
- Timeout: Maximum time the provider allows a function to run before terminating it.
Benefits of serverless architecture
1. Zero responsibility for server management
The basis of serverless computing is that the servers your application will use are handled by a third-party such as a cloud provider. This helps you to focus on other aspects, such as the front end and user experience.
2. Scalable
There is a significant risk in investing in architecture on your own for your applications, as you never know initially what the outcome will be. Purchasing and maintaining servers can be heavy on resources, and expanding becomes more tedious when you want to develop your application. If you opt for serverless architecture, you won’t have to worry about these factors, and scalability becomes easier.
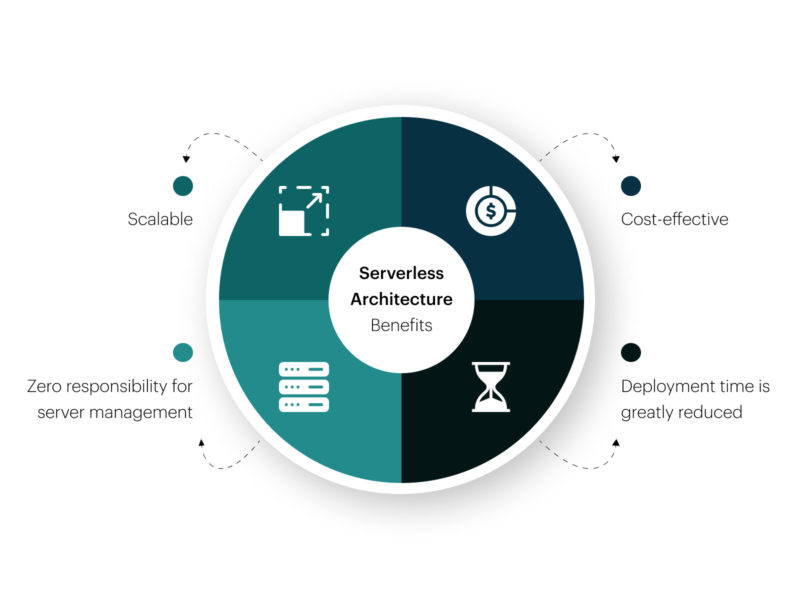
3. Cost-effective
One of the most significant advantages of this kind of architecture is the different areas where it helps to save money while providing the same quality of service. In traditional architecture, one needs to be safe and purchase extra servers in case of downtime or performance bottlenecks. Serverless architecture only charges you when it’s being used, i.e., when an event is triggered, which thus results in you paying only for the services you use.
The cloud provider also takes care of maintenance, and businesses don’t need to worry about hiring a specific team just for this purpose. This saves human resource costs also.
4. Deployment time is significantly reduced
The time taken for the product to reach the market is reduced by a significant amount, as the development environment is set up more efficiently, and there is no pressure from the backend side. The features are also shipped faster to the user, who receives the updates more quickly.
Challenges of serverless architecture
1. Vendor lock-in
Outsourcing the backend support to a third-party requires complete faith and trust in the vendor. You say get’s very limited, and you must rely on them for every service. If there is any problem, you can’t solve it on your terms and in a fast manner. You need to wait patiently for the service provider to solve it. Switching from one provider to another, from AWS Lambda to Azure, is also tricky.
2. Debugging and testing
For debugging and testing the application, it is essential to know how the backend works and where the error occurs. In serverless architecture, this is difficult to see completely. Integration tests are also more complex to perform since the environment is tough to replicate.
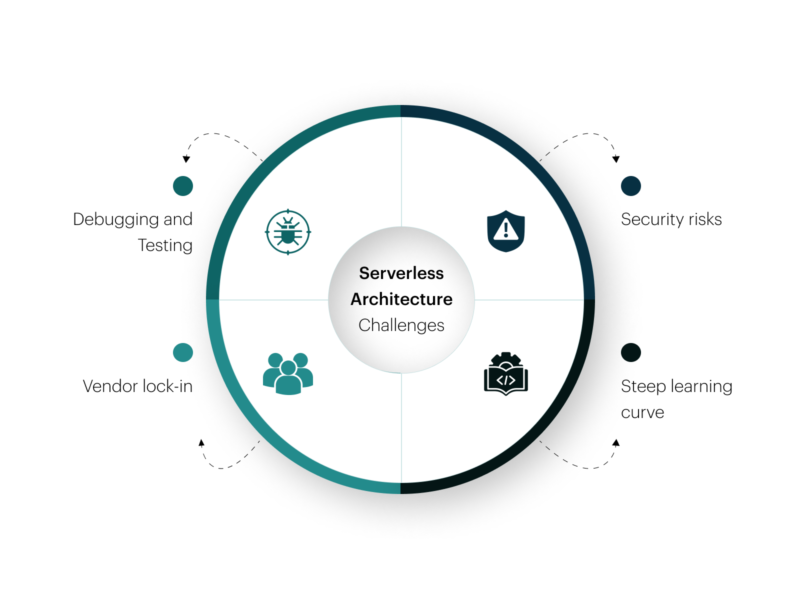
3. Security risks
Multiple clients access the server at the same time. There is a risk of a lack of data abstraction, and data can be compromised due to some fault in the infrastructure.
4. Steep learning curve
Understanding and learning about FaaS (Function as a service) can be pretty tricky and complicated despite the number of resources that are available on the Internet. Also, for implementing the serverless architecture, one needs to break the monolith structure into microservices which requires expertise and help from professionals to break it down smoothly.
Serverless Architecture vs. Container Architecture
Containers are lightweight and portable and run anything, from a small microservice to an extensive application. These contain all the codes for running it independently, from binary files to executables.
Some points with respect to which this type differs from serverless architecture are:
1. Longevity
In serverless, functions are triggered by an event. These are invoked for a short period of time and die after execution. The benefit is that it pushes apps to production faster. In container architecture, the containers are always running and do not die even after execution. They run for a prolonged period of time.
2. Supported host environments
Serverless architecture runs on particular hosting platforms provided mainly by cloud providers such as AWS Lambda. Container architecture can run on operating systems such as Windows and Linux servers.
3. Running locally
Serverless architecture cannot be run locally. It becomes highly complex to run it outside a public cloud platform. Container architecture can run on your local computers, and setting up its development environment on your workstation is easier.
4. Latency
In serverless architecture, the function invocation time is higher. You might face latency issues if multiple users try to access the same service. Containers have a much lower latency time. You need to send an HTTPS request, and also you’ll immediately get a response.
5. Cost
Serverless architecture is biller according to how you use it. Container architecture engines are open source and thus can be deployed on your local environment and run for free.
What does Markovate do?
It’s evident how shifting to serverless architecture can boost your business and take care of all the application backend support. It’s essential that the cloud provider is trustworthy and reliable, though, and we all know that one of the most prominent names in the field of cloud computing is Google cloud services.
Markovate, as a Google Cloud Development company, exploits its potential to the maximum to encompass as many services as possible. We provide deep expertise and professionals who offer adaptable and secure solutions using leading-edge technologies. Using Markovate’s experts, GCP integration can help ensure data security, zero downtime, and fault tolerance. We also provide API integration, data analytics, and end-to-end development services. Our various models can be adopted per your needs and requirements, whichever suits your business model the best. Our GCP App development follows several processes, from wireframing to testing and support, to ensure you have the best solution possible!
FAQs
1. What are the four core components of serverless development?
The four core components of serverless development are FaaS (Function As A Service), BaaS (Backend As A Service), API Gateway, and database.
2. Why can serverless architectures on clouds be functional in DevOps?
Serverless architecture for DevOps can be beneficial as it provides greater scalability, more flexibility, and a quicker time to release, all at a reduced cost.
3. Why serverless is the future?
Yes, serverless is the future, as the companies already adopted it have observed agility, operational benefits, and cost saving. Thus, no wonder more and more companies are shifting to this model to increase their business functionality.

















Discussion about this post